Regret is a universal human emotion, and the English language offers a rich vocabulary to express its nuances. Mastering adjectives that convey regret allows for more precise and impactful communication, whether in writing or speech. This article provides a comprehensive guide to adjectives for regret, exploring their meanings, usage, and structural patterns. This guide benefits English language learners, writers, and anyone seeking to enhance their emotional vocabulary.
By understanding these adjectives, you’ll be able to articulate feelings of remorse, disappointment, and self-reproach with greater accuracy and depth. This knowledge will not only improve your communication skills but also deepen your understanding of human emotions.
Table of Contents
- Definition of Adjectives for Regret
- Structural Breakdown
- Types and Categories of Adjectives for Regret
- Examples of Adjectives for Regret
- Usage Rules for Adjectives of Regret
- Common Mistakes
- Practice Exercises
- Advanced Topics
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Definition of Adjectives for Regret
Adjectives for regret are words that describe the feeling of sadness, disappointment, or remorse over something that has happened or been done (or not done) in the past. These adjectives modify nouns or pronouns to convey the intensity, cause, or nature of the regret being experienced. They add depth and specificity to expressions of remorse, allowing for a more nuanced portrayal of emotions.
Regret, as a concept, is closely tied to reflection and evaluation of past actions. Therefore, adjectives describing regret often carry connotations of self-reproach, disappointment, or longing for a different outcome. The choice of adjective can significantly impact the overall tone and meaning of a sentence.
These adjectives can be classified based on several factors, including the intensity of the regret they convey (mild, moderate, intense), the cause of the regret (e.g., a foolish decision), or the effect of the regret (e.g., a sorrowful mood). Understanding these classifications helps in selecting the most appropriate adjective for a given context.
Structural Breakdown
Adjectives for regret typically function as attributive or predicative adjectives. Attributive adjectives precede the noun they modify, while predicative adjectives follow a linking verb (e.g., is, are, was, were, seems).
Attributive Use: In this construction, the adjective directly modifies the noun, providing immediate context. For example:
- “She made a regretful decision.” (regretful modifies decision)
- “He carried a remorseful heart.” (remorseful modifies heart)
Predicative Use: Here, the adjective describes the subject of the sentence via a linking verb. For example:
- “She was ashamed of her actions.” (ashamed describes she)
- “He seemed penitent after the apology.” (penitent describes he)
Many adjectives of regret can also be used in participial phrases, adding another layer of complexity and expressiveness. For example:
- “Regretting his outburst, he apologized immediately.” (Regretting is a present participle.)
- “Haunted by her past mistakes, she sought redemption.” (Haunted is a past participle.)
The position and form of the adjective (attributive, predicative, participial) contribute to the overall flow and emphasis of the sentence. Choosing the right structure can enhance the emotional impact of the expression.
Types and Categories of Adjectives for Regret
Adjectives for regret can be categorized based on the intensity of the feeling they convey. This classification helps writers and speakers choose the most appropriate word to match the severity of the situation.
Adjectives for Mild Regret
These adjectives express a slight feeling of disappointment or remorse, often about minor issues.
- Slightly regretful: Indicates a small degree of regret.
- Mildly disappointed: Suggests a gentle feeling of letdown.
- A little sorry: Expresses a small amount of remorse.
- Somewhat remorseful: Similar to “a little sorry,” but slightly more formal.
- Displeased: Indicates a feeling of dissatisfaction.
Adjectives for Moderate Regret
These adjectives convey a more noticeable feeling of remorse or disappointment, often about more significant issues.
- Regretful: A general term for feeling regret.
- Disappointed: Indicates a more profound feeling of letdown than “mildly disappointed.”
- Remorseful: Expresses a deeper sense of guilt or sorrow.
- Sorry: A common and versatile term for feeling regret.
- Contrite: Suggests a sincere feeling of regret and a desire to make amends.
- Apologetic: Expressing regret and a willingness to apologize.
Adjectives for Intense Regret
These adjectives describe a strong, profound feeling of remorse, often associated with significant mistakes or losses.
- Ashamed: Indicates a feeling of humiliation or disgrace.
- Guilty: Expresses a strong feeling of responsibility for wrongdoing.
- Penitent: Suggests deep remorse and a commitment to change.
- Rueful: Expressing sorrow or regret in a humorous way.
- Heartbroken: Indicates extreme sadness and disappointment.
- Devastated: Feeling overwhelmed by grief or disappointment.
- Tormented: Experiencing severe mental or physical suffering due to regret.
- Wretched: Feeling extremely unhappy or unfortunate.
Adjectives Describing the Cause of Regret
These adjectives describe the nature of the action or event that caused the regret.
- Foolish: Describes an action that was unwise or silly.
- Imprudent: Describes an action that was not cautious or sensible.
- Reckless: Describes an action done without thought or care for the consequences.
- Careless: Describes an action done without sufficient attention.
- Negligent: Describes a failure to take proper care in doing something.
- Thoughtless: Describes an action done without considering the feelings of others.
- Rash: Describes an action done impulsively and without thinking.
- Ill-advised: Describes an action that was not a good idea.
Examples of Adjectives for Regret
The following tables provide examples of how adjectives for regret can be used in sentences, categorized by intensity.
Table 1: Examples of Adjectives for Mild Regret
This table presents sentences illustrating the use of adjectives denoting mild regret, showcasing their application in expressing slight disappointment or remorse.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Slightly regretful | She was slightly regretful about missing the party, but she had a good reason. |
| Mildly disappointed | He was mildly disappointed with the film, but overall, he enjoyed the experience. |
| A little sorry | I’m a little sorry I didn’t call you back sooner. |
| Somewhat remorseful | He felt somewhat remorseful that he hadn’t spent more time with his grandfather. |
| Displeased | She was displeased with the service at the restaurant. |
| Slightly regretful | He felt slightly regretful about not taking the job offer. |
| Mildly disappointed | They were mildly disappointed by the hotel room. |
| A little sorry | She was a little sorry for yelling at her brother. |
| Somewhat remorseful | He was somewhat remorseful for his harsh words. |
| Displeased | The manager was displeased with the employee’s performance. |
| Slightly regretful | I am slightly regretful I didn’t buy that dress when I had the chance. |
| Mildly disappointed | They were mildly disappointed that the concert was canceled. |
| A little sorry | He’s a little sorry he didn’t study harder for the exam. |
| Somewhat remorseful | She felt somewhat remorseful for her actions. |
| Displeased | The customer was displeased with the quality of the product. |
| Slightly regretful | We were slightly regretful that we missed the opportunity. |
| Mildly disappointed | She was mildly disappointed that her application was rejected. |
| A little sorry | I’m a little sorry I couldn’t make it to your party. |
| Somewhat remorseful | He was somewhat remorseful about the argument. |
| Displeased | The teacher was displeased with the student’s behavior. |
| Slightly regretful | She was slightly regretful for eating the entire cake. |
| Mildly disappointed | He was mildly disappointed in the ending of the book. |
| A little sorry | They were a little sorry they hadn’t brought a gift. |
| Somewhat remorseful | She was somewhat remorseful about the breakup. |
| Displeased | The audience was displeased with the performance. |
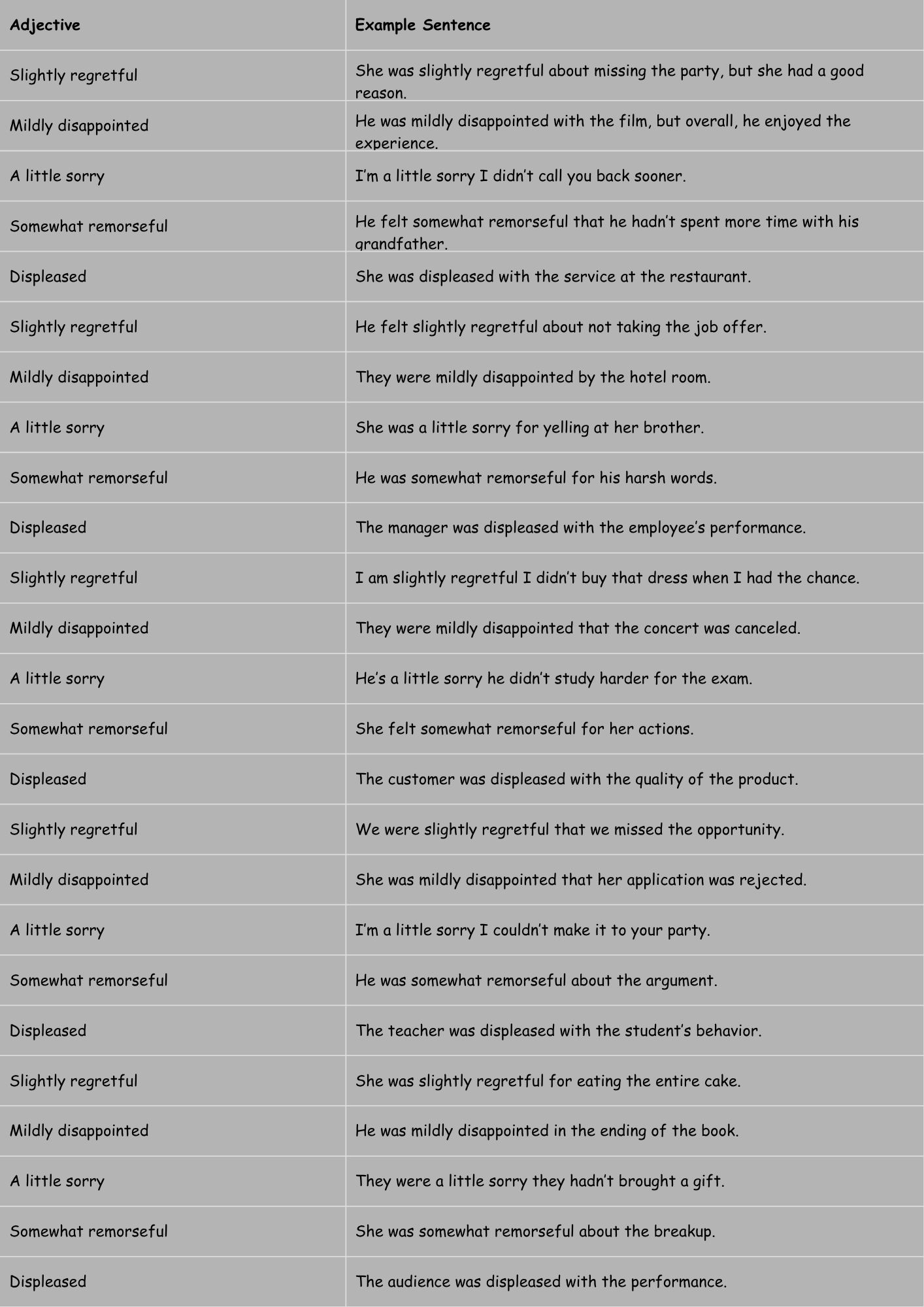
Table 2: Examples of Adjectives for Moderate Regret
This table illustrates how adjectives of moderate regret are employed in sentences to convey a more substantial sense of remorse or disappointment.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Regretful | She was regretful about her harsh words. |
| Disappointed | He was disappointed that he didn’t get the promotion. |
| Remorseful | The thief was remorseful for his actions. |
| Sorry | I’m sorry I hurt your feelings. |
| Contrite | The contrite student apologized to the teacher. |
| Apologetic | He gave an apologetic glance towards her. |
| Regretful | He felt regretful for not listening to his parents. |
| Disappointed | She was disappointed with the outcome of the election. |
| Remorseful | The criminal seemed genuinely remorseful. |
| Sorry | They were sorry to hear about his loss. |
| Contrite | The contrite sinner sought forgiveness. |
| Apologetic | His tone was apologetic when he explained the situation. |
| Regretful | We were regretful we couldn’t attend the wedding. |
| Disappointed | He was disappointed in his team’s performance. |
| Remorseful | She was remorseful for betraying her friend’s trust. |
| Sorry | We’re sorry for the inconvenience caused. |
| Contrite | The contrite employee admitted his mistake. |
| Apologetic | She sent an apologetic email to her boss. |
| Regretful | I am regretful for not saying goodbye. |
| Disappointed | They were disappointed with the service. |
| Remorseful | He was remorseful for his violent actions. |
| Sorry | She felt sorry for her neighbor’s troubles. |
| Contrite | The contrite witness confessed to the crime. |
| Apologetic | His apologetic letter expressed deep sorrow. |
| Regretful | She was regretful she hadn’t told him how she felt. |
Table 3: Examples of Adjectives for Intense Regret
This table provides examples of adjectives describing intense regret, illustrating their use to convey profound feelings of remorse, guilt, or despair.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Ashamed | He was ashamed of his behavior at the party. |
| Guilty | She felt guilty for lying to her parents. |
| Penitent | The penitent prisoner sought forgiveness. |
| Rueful | He gave a rueful smile as he recounted the story. |
| Heartbroken | She was heartbroken after the breakup. |
| Devastated | He was devastated by the news of her death. |
| Tormented | He was tormented by the memories of the war. |
| Wretched | She felt wretched after losing her job. |
| Ashamed | They were ashamed to admit their mistake. |
| Guilty | He felt guilty for not helping his friend. |
| Penitent | The penitent thief returned the stolen goods. |
| Rueful | He gave a rueful laugh. |
| Heartbroken | She was heartbroken when her pet died. |
| Devastated | They were devastated by the flood. |
| Tormented | She was tormented by nightmares. |
| Wretched | He felt wretched after the argument. |
| Ashamed | I was deeply ashamed of my outburst. |
| Guilty | She carried a guilty conscience for years. |
| Penitent | The penitent sinner knelt in prayer. |
| Rueful | He offered a rueful apology. |
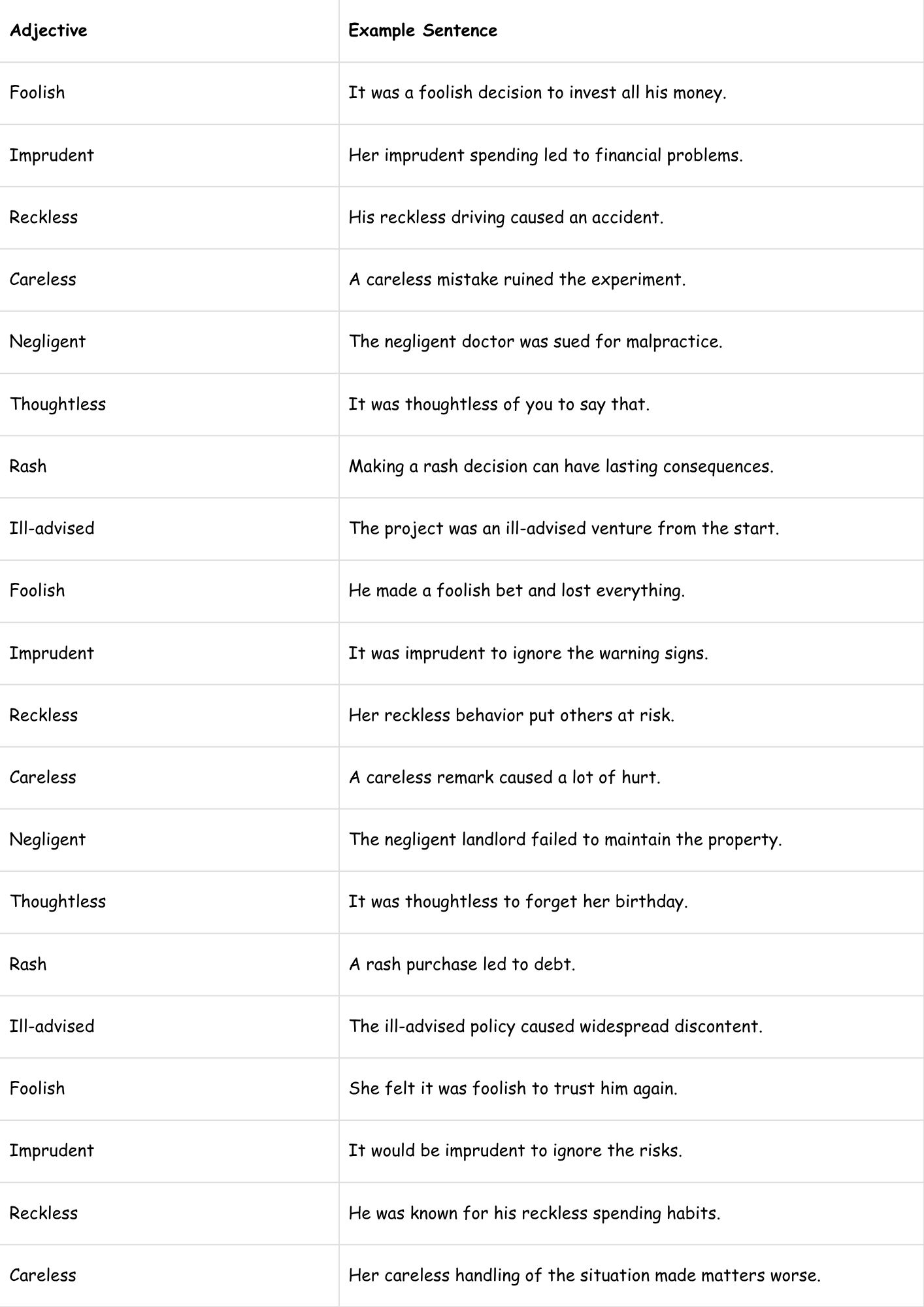
Table 4: Examples of Adjectives Describing the Cause of Regret
This table shows how adjectives are used to describe the nature of the action or event that led to feelings of regret.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Foolish | It was a foolish decision to invest all his money. |
| Imprudent | Her imprudent spending led to financial problems. |
| Reckless | His reckless driving caused an accident. |
| Careless | A careless mistake ruined the experiment. |
| Negligent | The negligent doctor was sued for malpractice. |
| Thoughtless | It was thoughtless of you to say that. |
| Rash | Making a rash decision can have lasting consequences. |
| Ill-advised | The project was an ill-advised venture from the start. |
| Foolish | He made a foolish bet and lost everything. |
| Imprudent | It was imprudent to ignore the warning signs. |
| Reckless | Her reckless behavior put others at risk. |
| Careless | A careless remark caused a lot of hurt. |
| Negligent | The negligent landlord failed to maintain the property. |
| Thoughtless | It was thoughtless to forget her birthday. |
| Rash | A rash purchase led to debt. |
| Ill-advised | The ill-advised policy caused widespread discontent. |
| Foolish | She felt it was foolish to trust him again. |
| Imprudent | It would be imprudent to ignore the risks. |
| Reckless | He was known for his reckless spending habits. |
| Careless | Her careless handling of the situation made matters worse. |
Usage Rules for Adjectives of Regret
When using adjectives for regret, it’s vital to consider the context and the specific nuance you want to convey. Here are some general usage rules:
- Choose the right intensity: Select an adjective that accurately reflects the degree of regret you wish to express. Using an adjective that is too strong or too weak can misrepresent your feelings.
- Consider the cause: If you want to emphasize the reason for the regret, use an adjective that describes the nature of the action or event that caused it.
- Pay attention to connotation: Some adjectives carry specific connotations. For example, “ashamed” implies a sense of humiliation, while “remorseful” suggests a deeper sense of guilt.
- Use correct grammar: Ensure that the adjective is used in the correct grammatical context, either attributively or predicatively.
- Avoid redundancy: Do not use multiple adjectives that express the same degree of regret. Choose the single most appropriate adjective.
Exceptions and Special Cases:
- Some adjectives, like “sorry,” can be used in various contexts and with different intensities. The meaning can be inferred from the surrounding words and the overall tone.
- In formal writing, consider using more precise and nuanced adjectives to convey subtle differences in emotion.
- In informal speech, simpler and more common adjectives may be more appropriate.
Common Mistakes
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using adjectives for regret:
1. Using the wrong intensity:
- Incorrect: “I’m devastated that I missed the bus.” (Devastated is too strong for a minor inconvenience.)
- Correct: “I’m disappointed that I missed the bus.”
2. Misusing “regretful” and “regrettable”:
- Incorrect: “The accident was very regretful.” (Regretful describes a person, not an event.)
- Correct: “The accident was very regrettable.” (Regrettable describes something that causes regret.)
3. Incorrect placement of adjectives:
- Incorrect: “She felt the decision foolish.” (Incorrect word order)
- Correct: “She felt the foolish decision.” (Attributive use)
- Correct: “She felt the decision was foolish.” (Predicative use)
4. Using redundant adjectives:
- Incorrect: “He was very sad and heartbroken.” (Heartbroken already implies a high degree of sadness.)
- Correct: “He was heartbroken.”
Table 5: Common Mistakes and Corrections
This table highlights common errors in using adjectives of regret and provides the corrected versions.
| Incorrect Sentence | Correct Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| I’m devastated I forgot to buy milk. | I’m disappointed I forgot to buy milk. | “Devastated” is too strong for forgetting milk. |
| The loss of the game was very regretful. | The loss of the game was very regrettable. | “Regretful” describes a person; “regrettable” describes an event. |
| She felt the action foolish. | She felt the foolish action. | Corrected word order for attributive adjective. |
| He was sad and heartbroken about the news. | He was heartbroken about the news. | “Heartbroken” already implies sadness. |
| I am feeling very ashamed for my mistake. | I am feeling very ashamed of my mistake. | Correct preposition to use with “ashamed.” |
| He was regretful for his behavior. | He was regretful about his behavior. | Correct preposition to use with “regretful.” |
| She felt guilty about to lie. | She felt guilty about lying. | Correct gerund form after “about.” |
| I am sorry for that I did. | I am sorry for what I did. | Correct use of “what” as a relative pronoun. |
| He was so remorseful of his actions. | He was so remorseful for his actions. | Correct preposition to use with “remorseful.” |
| I am very contrite for what I have done. | I am very contrite about what I have done. | Correct preposition to use with “contrite.” |
Practice Exercises
Exercise 1: Fill in the Blanks
Choose the most appropriate adjective from the list to fill in the blank in each sentence.
(regretful, ashamed, disappointed, remorseful, sorry)
- She was __________ that she missed her daughter’s graduation.
- He felt __________ for his cruel words.
- I am __________ that I can’t attend your wedding.
- They were __________ in their team’s performance.
- He was __________ of his behavior at the meeting.
Exercise 2: Sentence Completion
Complete each sentence with an appropriate adjective for regret.
- After realizing his mistake, he felt __________.
- The __________ student apologized to the teacher.
- She was __________ that the trip was canceled.
- He offered a __________ smile as he remembered the incident.
- The __________ criminal confessed to the crime.
Exercise 3: Error Correction
Identify and correct the errors in the following sentences.
- I’m devastated I didn’t get the job.
- The accident was very regretful.
- She felt the decision foolish.
- He was sad and heartbroken.
- I am feeling very ashamed for my mistake.
Exercise 4: Sentence Rewriting
Rewrite the following sentences using a different adjective for regret with a similar meaning.
- She was sorry for her actions.
- He was disappointed with the outcome.
- I am ashamed of my behavior.
- They were regretful for not trying harder.
- He felt guilty about lying.
Table 6: Practice Exercise Answers
This table provides the answers to the practice exercises, allowing learners to check their understanding and progress.
| Exercise | Question | Answer |
|---|---|---|
| Exercise 1 | 1. She was __________ that she missed her daughter’s graduation. | regretful |
| 2. He felt __________ for his cruel words. | remorseful | |
| 3. I am __________ that I can’t attend your wedding. | sorry | |
| 4. They were __________ in their team’s performance. | disappointed | |
| 5. He was __________ of his behavior at the meeting. | ashamed | |
| Exercise 2 | 1. After realizing his mistake, he felt __________. | remorseful/ashamed/guilty |
| 2. The __________ student apologized to the teacher. | contrite | |
| 3. She was __________ that the trip was canceled. | disappointed | |
| 4. He offered a __________ smile as he remembered the incident. | rueful | |
| 5. The __________ criminal confessed to the crime. | penitent | |
| Exercise 3 | 1. I’m devastated I didn’t get the job. | I’m disappointed I didn’t get the job. |
| 2. The accident was very regretful. | The accident was very regrettable. | |
| 3. She felt the decision foolish. | She felt the foolish decision. Or: She felt the decision was foolish. | |
| 4. He was sad and heartbroken. | He was heartbroken. | |
| 5. I am feeling very ashamed for my mistake. | I am feeling very ashamed of my mistake. | |
| Exercise 4 | 1. She was sorry for her actions. | She was regretful for her actions. / She was remorseful for her actions. |
| 2. He was disappointed with the outcome. | He was displeased with the outcome. / He was regretful about the outcome. | |
| 3. I am ashamed of my behavior. | I am guilty of my behavior. / I am contrite about my behavior. | |
| 4. They were regretful for not trying harder. | They were disappointed for not trying harder. / They were remorseful for not trying harder. | |
| 5. He felt guilty about lying. | He felt ashamed about lying. / He felt remorseful about lying. |
Advanced Topics
For advanced learners, exploring the nuances of adjectives for regret can involve delving into literary analysis, psychological contexts, and cross-cultural comparisons.
- Literary Analysis: Examine how authors use adjectives of regret to develop characters, create atmosphere, and convey themes. Consider how the choice of adjective contributes to the overall impact of a passage.
- Psychological Contexts: Investigate the psychological implications of different types of regret. Explore how adjectives can reflect underlying emotional states like guilt, shame, and self-reproach.
- Cross-Cultural Comparisons: Compare how different cultures express regret and how this is reflected in their languages. Consider whether certain adjectives have equivalents in other languages and whether the connotations are the same.
- Figurative Language: Explore how adjectives for regret can be used metaphorically or symbolically. For example, a “haunted” landscape might represent the lingering effects of past mistakes.
FAQ
Q1: What is the difference between “regretful” and “regrettable”?
A: “Regretful” describes a person who feels regret, while “regrettable” describes something that causes regret. For example, “She was regretful about her decision,” but “It was a regrettable mistake.”
Q2: How do I choose the right adjective for regret?
A: Consider the intensity of the feeling you want to convey, the cause of the regret, and the specific nuance you want to express. Think about whether you want to emphasize guilt, shame, disappointment, or another related emotion.
Q3: Can “sorry” be used for both mild and intense regret?
A: Yes, “sorry” is a versatile word that can convey a range of emotions, from mild disappointment to deep remorse. The context and tone of voice will determine the intensity of the feeling.
Q4: What prepositions are commonly used with adjectives for regret?
A: Common prepositions include “about,” “for,” and “of.” For example, “ashamed of,” “sorry for,” “regretful about.” The correct preposition depends on the specific adjective and the grammatical structure of the sentence.
Q5: Is it possible to overuse adjectives for regret?
A: Yes, overuse can make your writing or speech sound melodramatic or insincere. Use adjectives sparingly and choose them carefully to maximize their impact.
Q6: What is the difference between “remorseful” and “penitent”?
A: Both adjectives express deep regret, but “penitent” implies a stronger commitment to change and a desire to make amends. “Remorseful” focuses more on the feeling of sorrow or guilt.
Q7: How can I improve my vocabulary of adjectives for regret?
A: Read widely, pay attention to how authors use adjectives to convey emotion, and practice using new words in your own writing and speech. Use a thesaurus to explore synonyms and related terms.
Q8: Are there any cultural differences in how regret is expressed?
A: Yes, different cultures may have different norms and expectations regarding the expression of regret. Some cultures may be more reserved, while others may be more open and expressive. This can influence the choice of adjectives and the overall tone of communication.
Conclusion
Mastering adjectives for regret enhances your ability to express complex emotions with precision and depth. By understanding the nuances of these adjectives, their structural usage, and common pitfalls, you can communicate more effectively
and empathetically. Continue to practice and refine your understanding of these words to enrich your vocabulary and emotional intelligence.



