Adjectives are essential for painting vivid pictures with words, and when describing people, they become even more crucial. Understanding which adjectives to use and how to use them effectively can significantly enhance your communication skills, allowing you to express nuances and subtleties in your descriptions. This article provides a comprehensive guide to adjectives used to describe people, covering various categories, usage rules, common mistakes, and practice exercises. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced learner, this resource will help you master the art of describing human characteristics with precision and flair.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Adjectives for Humans
- Structural Breakdown
- Types of Adjectives for Humans
- Examples of Adjectives for Humans
- Usage Rules for Adjectives
- Common Mistakes
- Practice Exercises
- Advanced Topics
- FAQ
- Conclusion
Introduction
Describing people effectively is a fundamental skill in communication, whether in writing or speaking. Adjectives play a crucial role in providing detailed and specific information about an individual’s characteristics, allowing us to create a vivid and accurate portrayal. This article focuses specifically on adjectives used to describe humans, covering a wide range of categories such as physical appearance, personality traits, emotional states, and more. Mastering these adjectives will not only enhance your vocabulary but also improve your ability to express yourself with greater precision and impact.
This guide is designed for English language learners of all levels, from beginners seeking to expand their basic vocabulary to advanced learners aiming to refine their descriptive skills. By understanding the different types of adjectives, their proper usage, and common pitfalls to avoid, you’ll be well-equipped to describe people in a compelling and accurate manner. Let’s delve into the world of adjectives and unlock the power of descriptive language!
Definition of Adjectives for Humans
An adjective is a word that modifies a noun or pronoun, providing additional information about its qualities or characteristics. When we talk about “adjectives for humans,” we specifically refer to adjectives that describe aspects of a person, such as their physical appearance, personality, emotions, intellect, social skills, and moral character. These adjectives help us paint a more complete and nuanced picture of an individual, going beyond simple identification to convey their unique attributes.
Adjectives can be classified based on their function and meaning. For example, some adjectives describe physical attributes like tall, short, or beautiful. Others describe personality traits like kind, generous, or ambitious. Understanding these classifications can help you choose the most appropriate adjective to convey the intended meaning.
In addition to their descriptive function, adjectives also play a crucial role in adding depth and richness to our language. They allow us to express subtle differences in meaning and to create more engaging and evocative descriptions. For instance, instead of simply saying someone is “happy,” we can use adjectives like joyful, delighted, or content to convey different shades of happiness.
Structural Breakdown
Understanding the structure of how adjectives are used in sentences is key to using them correctly. Adjectives typically appear in one of two positions: attributive or predicative. The attributive position is before the noun they modify, while the predicative position is after a linking verb (such as be, seem, appear).
Attributive Adjectives: These adjectives directly precede the noun they modify. For example, in the phrase “a kind woman,” the adjective “kind” comes before the noun “woman.” This is the most common way to use adjectives.
Predicative Adjectives: These adjectives follow a linking verb and describe the subject of the sentence. For example, in the sentence “She is intelligent,” the adjective “intelligent” follows the linking verb “is” and describes the subject “she.”
It’s also important to note that some adjectives can only be used attributively (e.g., chief, main), while others can only be used predicatively (e.g., afraid, alike). Most adjectives, however, can be used in both positions. Understanding these structural differences will help you use adjectives more effectively and avoid common grammatical errors.
Types of Adjectives for Humans
Adjectives for humans can be categorized based on the aspect of a person they describe. Here are some of the main categories:
Physical Appearance
These adjectives describe a person’s physical attributes, such as their height, weight, build, hair color, eye color, and overall appearance. Examples include: tall, short, thin, overweight, muscular, beautiful, handsome, pretty, ugly, old, young, blonde, brunette, blue-eyed, well-dressed, and unkempt.
Personality Traits
These adjectives describe a person’s characteristic behaviors, attitudes, and qualities. Examples include: kind, generous, selfish, arrogant, humble, outgoing, introverted, optimistic, pessimistic, honest, dishonest, brave, cowardly, loyal, disloyal, ambitious, lazy, hardworking, and creative.
Emotional State
These adjectives describe a person’s current emotional condition or mood. Examples include: happy, sad, angry, excited, bored, anxious, calm, relaxed, stressed, depressed, cheerful, gloomy, content, frustrated, jealous, lonely, nervous, overwhelmed, peaceful, and tired.
Intellectual Abilities
These adjectives describe a person’s cognitive skills, knowledge, and intelligence. Examples include: intelligent, smart, clever, brilliant, wise, knowledgeable, educated, ignorant, foolish, naive, logical, analytical, creative, imaginative, perceptive, insightful, studious, bookish, sharp, and dull.
Social Qualities
These adjectives describe a person’s ability to interact with others and their social behavior. Examples include: friendly, sociable, outgoing, reserved, shy, polite, rude, considerate, inconsiderate, helpful, unhelpful, cooperative, competitive, generous, selfish, charming, awkward, tactful, boastful, and humble.
Moral Character
These adjectives describe a person’s ethical principles and moral values. Examples include: honest, trustworthy, loyal, dishonest, deceitful, corrupt, ethical, principled, virtuous, wicked, just, unjust, compassionate, merciless, responsible, irresponsible, respectful, disrespectful, courageous, and cowardly.
Examples of Adjectives for Humans
To further illustrate the use of adjectives for humans, here are several examples organized by category.
Physical Appearance Examples
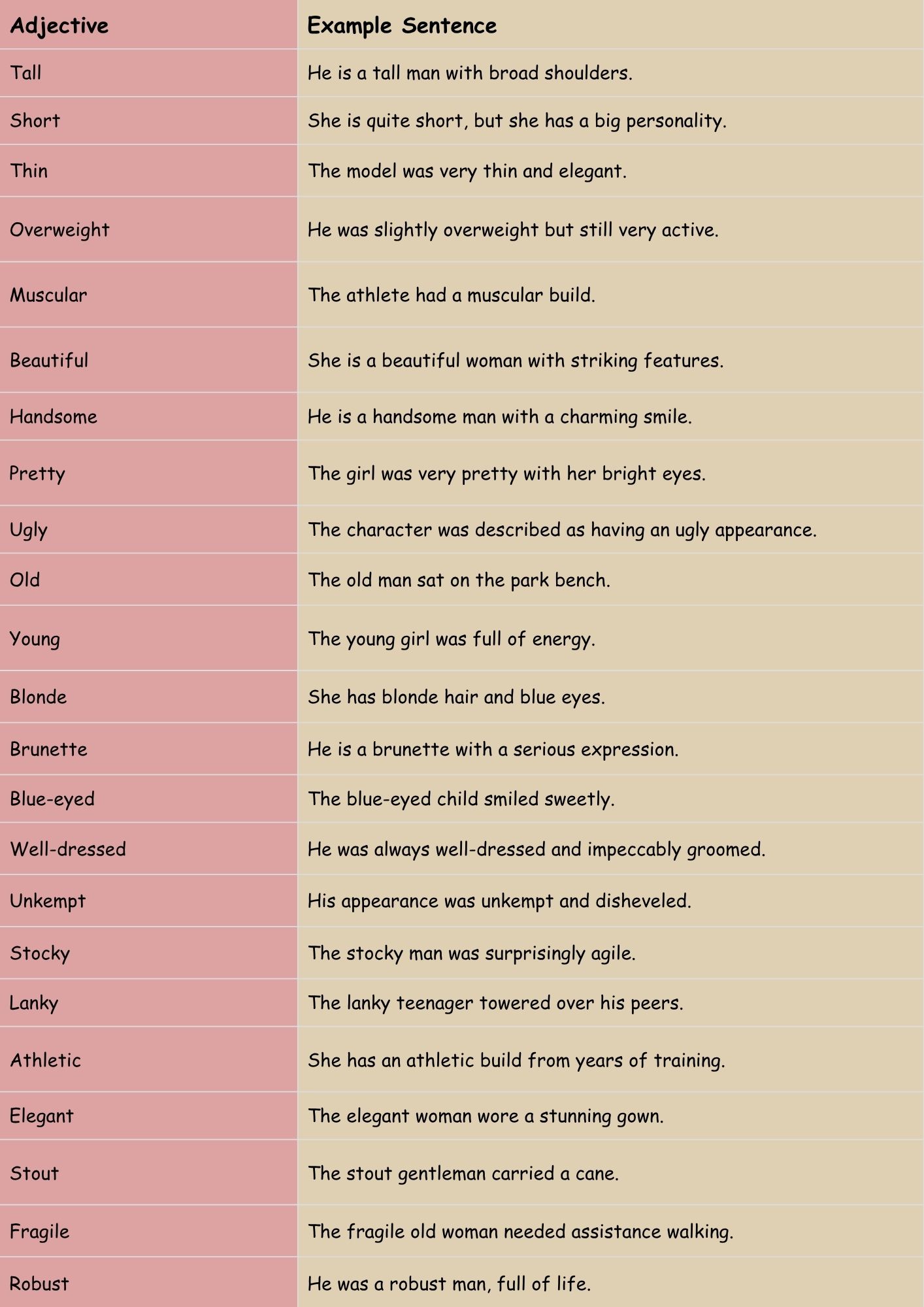
The following table provides examples of adjectives describing physical appearance, along with example sentences demonstrating their usage.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Tall | He is a tall man with broad shoulders. |
| Short | She is quite short, but she has a big personality. |
| Thin | The model was very thin and elegant. |
| Overweight | He was slightly overweight but still very active. |
| Muscular | The athlete had a muscular build. |
| Beautiful | She is a beautiful woman with striking features. |
| Handsome | He is a handsome man with a charming smile. |
| Pretty | The girl was very pretty with her bright eyes. |
| Ugly | The character was described as having an ugly appearance. |
| Old | The old man sat on the park bench. |
| Young | The young girl was full of energy. |
| Blonde | She has blonde hair and blue eyes. |
| Brunette | He is a brunette with a serious expression. |
| Blue-eyed | The blue-eyed child smiled sweetly. |
| Well-dressed | He was always well-dressed and impeccably groomed. |
| Unkempt | His appearance was unkempt and disheveled. |
| Stocky | The stocky man was surprisingly agile. |
| Lanky | The lanky teenager towered over his peers. |
| Athletic | She has an athletic build from years of training. |
| Elegant | The elegant woman wore a stunning gown. |
| Stout | The stout gentleman carried a cane. |
| Fragile | The fragile old woman needed assistance walking. |
| Robust | He was a robust man, full of life. |
Personality Traits Examples
The following table provides examples of adjectives describing personality traits, along with example sentences demonstrating their usage.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Kind | She is a kind and compassionate person. |
| Generous | He is always generous with his time and resources. |
| Selfish | His selfish behavior alienated his friends. |
| Arrogant | The arrogant CEO was difficult to work with. |
| Humble | Despite his success, he remained humble and grounded. |
| Outgoing | She is an outgoing and sociable individual. |
| Introverted | He is quiet and introverted, preferring to read. |
| Optimistic | She maintains an optimistic outlook on life. |
| Pessimistic | He tends to be pessimistic about the future. |
| Honest | She is known for being honest and trustworthy. |
| Dishonest | His dishonest actions damaged his reputation. |
| Brave | The brave firefighter risked his life to save others. |
| Cowardly | His cowardly behavior was disappointing. |
| Loyal | She is a loyal friend who always stands by you. |
| Disloyal | His disloyal actions betrayed their trust. |
| Ambitious | He is an ambitious young professional. |
| Lazy | His lazy attitude prevented him from achieving his goals. |
| Hardworking | She is a hardworking student who excels in her studies. |
| Creative | He is a creative artist with a unique vision. |
| Witty | She’s a witty conversationalist who always makes people laugh. |
| Charming | He is a charming man who can win anyone over. |
| Grumpy | The grumpy old man complained about everything. |
| Patient | She is a patient teacher who understands her students. |
Emotional State Examples
The following table provides examples of adjectives describing emotional state, along with example sentences demonstrating their usage.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Happy | She looked happy and content. |
| Sad | He felt sad after the movie ended. |
| Angry | She was angry about the unfair decision. |
| Excited | The children were excited about the trip. |
| Bored | He felt bored during the long lecture. |
| Anxious | She was anxious about the upcoming exam. |
| Calm | He remained calm despite the chaos. |
| Relaxed | She felt relaxed after her vacation. |
| Stressed | He was stressed about the deadline. |
| Depressed | She felt depressed after the breakup. |
| Cheerful | She is always cheerful and optimistic. |
| Gloomy | He was gloomy because of the bad weather. |
| Content | She felt content with her simple life. |
| Frustrated | He was frustrated with the slow internet. |
| Jealous | She felt jealous of her friend’s success. |
| Lonely | He felt lonely after moving to a new city. |
| Nervous | She was nervous before her presentation. |
| Overwhelmed | He felt overwhelmed by the amount of work. |
| Peaceful | She felt peaceful in the quiet countryside. |
| Tired | He was tired after a long day. |
| Annoyed | She was annoyed by the constant noise. |
| Delighted | He was delighted to hear the good news. |
| Hopeful | She felt hopeful about the future. |
Intellectual Abilities Examples
The following table provides examples of adjectives describing intellectual abilities, along with example sentences demonstrating their usage.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Intelligent | She is an intelligent student who excels in all subjects. |
| Smart | He is a smart businessman who always makes wise decisions. |
| Clever | She is a clever strategist who can solve any problem. |
| Brilliant | He is a brilliant scientist who has made groundbreaking discoveries. |
| Wise | She is a wise counselor who gives excellent advice. |
| Knowledgeable | He is a knowledgeable historian who knows everything about the past. |
| Educated | She is an educated professional with a degree in engineering. |
| Ignorant | He is ignorant about current events and world affairs. |
| Foolish | It was a foolish decision to invest in that risky venture. |
| Naive | She is naive and easily trusts everyone she meets. |
| Logical | He has a logical mind and can analyze situations effectively. |
| Analytical | She is an analytical thinker who pays attention to detail. |
| Creative | He is a creative writer with a vivid imagination. |
| Imaginative | She is an imaginative storyteller who captivates her audience. |
| Perceptive | He is a perceptive observer who notices subtle details. |
| Insightful | She is an insightful analyst who understands complex issues. |
| Studious | He is a studious scholar who spends hours in the library. |
| Bookish | She is a bookish girl who loves to read. |
| Sharp | He has a sharp mind and learns quickly. |
| Dull | His performance was dull and uninspired. |
Social Qualities Examples
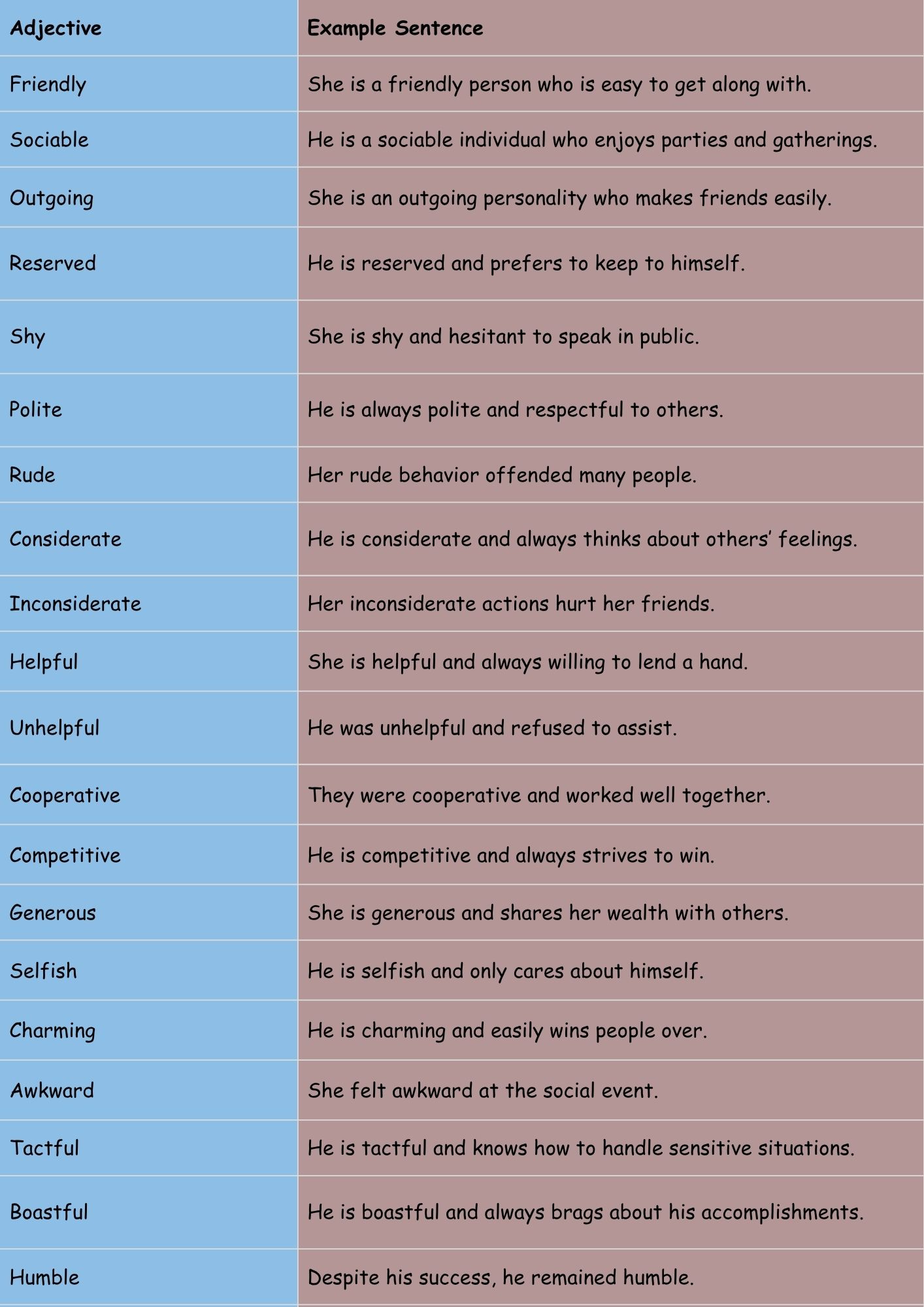
The following table provides examples of adjectives describing social qualities, along with example sentences demonstrating their usage.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Friendly | She is a friendly person who is easy to get along with. |
| Sociable | He is a sociable individual who enjoys parties and gatherings. |
| Outgoing | She is an outgoing personality who makes friends easily. |
| Reserved | He is reserved and prefers to keep to himself. |
| Shy | She is shy and hesitant to speak in public. |
| Polite | He is always polite and respectful to others. |
| Rude | Her rude behavior offended many people. |
| Considerate | He is considerate and always thinks about others’ feelings. |
| Inconsiderate | Her inconsiderate actions hurt her friends. |
| Helpful | She is helpful and always willing to lend a hand. |
| Unhelpful | He was unhelpful and refused to assist. |
| Cooperative | They were cooperative and worked well together. |
| Competitive | He is competitive and always strives to win. |
| Generous | She is generous and shares her wealth with others. |
| Selfish | He is selfish and only cares about himself. |
| Charming | He is charming and easily wins people over. |
| Awkward | She felt awkward at the social event. |
| Tactful | He is tactful and knows how to handle sensitive situations. |
| Boastful | He is boastful and always brags about his accomplishments. |
| Humble | Despite his success, he remained humble. |
Moral Character Examples
The following table provides examples of adjectives describing moral character, along with example sentences demonstrating their usage.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Honest | She is an honest person who always tells the truth. |
| Trustworthy | He is a trustworthy friend who never breaks his promises. |
| Loyal | She is a loyal supporter who always stands by her friends. |
| Dishonest | He is a dishonest businessman who deceives his customers. |
| Deceitful | She is a deceitful liar who cannot be trusted. |
| Corrupt | He is a corrupt politician who accepts bribes. |
| Ethical | She is an ethical journalist who reports the truth. |
| Principled | He is a principled leader who stands up for his beliefs. |
| Virtuous | She is a virtuous woman who lives a moral life. |
| Wicked | He is a wicked villain who commits evil deeds. |
| Just | He is a just judge who delivers fair verdicts. |
| Unjust | The unjust law discriminated against minorities. |
| Compassionate | She is a compassionate nurse who cares for her patients. |
| Merciless | He is a merciless tyrant who shows no pity. |
| Responsible | She is a responsible parent who takes care of her children. |
| Irresponsible | He is an irresponsible driver who causes accidents. |
| Respectful | She is respectful of elders and authority figures. |
| Disrespectful | He is disrespectful and shows no regard for others. |
| Courageous | He is a courageous soldier who fights for his country. |
| Cowardly | He is a cowardly person who runs away from danger. |
Usage Rules for Adjectives
Using adjectives correctly involves understanding a few key rules.
Attributive vs. Predicative Use
As mentioned earlier, adjectives can be used attributively (before the noun) or predicatively (after a linking verb). Some adjectives are more commonly used in one position than the other. For example, “elder” is typically used attributively (“the elder statesman”), while “afraid” is typically used predicatively (“She is afraid”).
It’s important to choose the correct structure to ensure clarity and grammatical accuracy. Misusing adjectives in the wrong position can lead to awkward or incorrect sentences.
Order of Adjectives
When using multiple adjectives to describe a noun, there is a general order to follow. This order, while not always strictly enforced, helps to ensure clarity and natural-sounding sentences. The typical order is:
- Opinion: beautiful, ugly, interesting
- Size: big, small, large
- Age: old, young, new
- Shape: round, square, rectangular
- Color: red, blue, green
- Origin: American, Italian, French
- Material: wooden, metal, plastic
- Purpose: sleeping (bag), writing (desk)
For example: “a beautiful large old round blue Italian wooden table.” While this example includes many adjectives, it illustrates the typical order. In practice, it’s best to use only a few well-chosen adjectives to avoid overwhelming the reader.
Comparative and Superlative Forms
Adjectives can be used to compare two or more things using comparative and superlative forms. The comparative form compares two things, while the superlative form compares three or more things.
For most short adjectives (one or two syllables), the comparative is formed by adding “-er” and the superlative by adding “-est.” For example: tall, taller, tallest; smart, smarter, smartest.
For longer adjectives (three or more syllables), the comparative is formed by using “more” and the superlative by using “most.” For example: beautiful, more beautiful, most beautiful; intelligent, more intelligent, most intelligent.
Some adjectives have irregular comparative and superlative forms. For example: good, better, best; bad, worse, worst.
Common Mistakes
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using adjectives for humans:
- Misusing attributive and predicative adjectives:
- Incorrect: “The afraid child hid.”
- Correct: “The child was afraid and hid.”
- Incorrect adjective order:
- Incorrect: “a metal old chair”
- Correct: “an old metal chair”
- Incorrect comparative/superlative forms:
- Incorrect: “more kinder”
- Correct: “kinder”
- Incorrect: “most happiest”
- Correct: “happiest”
- Using adjectives that don’t accurately reflect the meaning:
- Incorrect: “He is a happy person, but he’s always crying.”
- Correct: “He is a sad person, despite his attempts to appear happy.”
Practice Exercises
Test your understanding of adjectives for humans with these practice exercises.
Exercise 1: Identifying Adjectives
Identify the adjectives that describe humans in the following sentences.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The kind woman helped the elderly man cross the street. | kind, elderly |
| 2. The intelligent student aced the difficult exam. | intelligent, difficult |
| 3. She is a beautiful and charming actress. | beautiful, charming |
| 4. The lazy employee was fired for his poor performance. | lazy, poor |
| 5. He is a brave firefighter who saves lives. | brave |
| 6. The nervous child clung to his mother’s leg. | nervous |
| 7. The selfish man refused to share his food. | selfish |
| 8. She is a creative artist with a unique style. | creative, unique |
| 9. The dishonest politician was caught in a scandal. | dishonest |
| 10. He is a humble and generous philanthropist. | humble, generous |
Exercise 2: Using Adjectives in Sentences
Fill in the blanks with appropriate adjectives to describe the people in the following sentences.
| Question | Answer | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. The __________ girl smiled at me. | friendly/happy | |
| 2. He is a __________ and __________ leader. | strong/wise | |
| 3. The __________ old house stood on the hill. | dilapidated/creaky | |
| 4. She is known for her __________ and __________ nature. | kind/compassionate | |
| 5. The __________ child threw a tantrum in the store. | spoiled/angry | |
| 6. He is a __________ and | __________ employee. | hardworking/dedicated |
Exercise 3: Choosing the Right Adjective
Choose the most appropriate adjective from the options provided to complete the following sentences.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. She is a __________ (smart/intelligent/wise) student who excels in all her subjects. | intelligent |
| 2. He is a __________ (brave/courageous/fearless) soldier who has received many awards. | courageous |
| 3. The __________ (happy/joyful/elated) children played in the park. | happy |
| 4. She is a __________ (kind/generous/benevolent) woman who donates to many charities. | generous |
| 5. He is a __________ (selfish/greedy/avaricious) man who only cares about money. | selfish |
Advanced Topics
For those looking to deepen their understanding of adjectives, here are some advanced topics.
Adjectives with Nuance
Some adjectives carry subtle nuances that can significantly impact the meaning of a sentence. For example, “thrifty” and “stingy” both describe someone who is careful with money, but “thrifty” has a positive connotation, while “stingy” has a negative one. Similarly, “assertive” and “aggressive” both describe someone who is forceful, but “assertive” is generally seen as a positive trait, while “aggressive” is not.
Understanding these nuances requires careful attention to context and a broad vocabulary. It’s also helpful to consult a dictionary or thesaurus to explore the subtle differences between similar adjectives.
Figurative Language with Adjectives
Adjectives can be used in figurative language to create more vivid and imaginative descriptions. For example, metaphors and similes often use adjectives to compare one thing to another: “He is as brave as a lion” (simile), “She has a heart of gold” (metaphor).
Personification, another form of figurative language, involves giving human qualities to inanimate objects or abstract concepts. Adjectives play a crucial role in personification, as they are used to describe these non-human entities in human terms: “The angry storm raged on.”
By mastering the use of adjectives in figurative language, you can add depth, color, and emotional impact to your writing and speaking.
FAQ
What is the difference between an adjective and an adverb?
An adjective modifies a noun or pronoun, whereas an adverb modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. For example, “She is a quick runner” (adjective) vs. “She runs quickly” (adverb).
Can a noun be used as an adjective?
Yes, nouns can sometimes function as adjectives. This is known as a noun adjunct or attributive noun. For example, “a computer programmer” (computer is a noun acting as an adjective).
How do I choose the right adjective to describe someone?
Consider the specific qualities or characteristics you want to emphasize. Think about the context and the overall impression you want to create. Use a thesaurus to explore synonyms and find the most appropriate word.
Are there any adjectives that should be avoided when describing people?
Avoid using adjectives that are offensive, discriminatory, or based on stereotypes. Be mindful of the impact your words can have and strive to use language that is respectful and inclusive.
How can I improve my vocabulary of adjectives for humans?
Read widely, pay attention to the language used by skilled writers and speakers, and make a habit of looking up unfamiliar words. Practice using new adjectives in your own writing and speaking.
Conclusion
Adjectives are powerful tools for describing people and conveying their unique qualities and characteristics. By mastering the different types of adjectives, understanding their usage rules, and avoiding common mistakes, you can significantly enhance your communication skills. Whether you’re writing a novel, giving a presentation, or simply conversing with friends, a strong command of adjectives will enable you to express yourself with greater precision, clarity, and impact. So, continue to explore the rich world of adjectives and unlock the power of descriptive language!



