Adjectives are powerful tools that allow us to paint vivid pictures with words. When it comes to describing men, selecting the right adjectives can be particularly impactful. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and using adjectives effectively to describe male characteristics, personalities, appearances, and more. Mastering these adjectives will enhance your communication skills, allowing you to express yourself with greater precision and nuance. Whether you’re a student, writer, or simply someone looking to improve their vocabulary, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and resources you need.
This article is designed for English language learners, writers, and anyone interested in expanding their vocabulary for describing men. We will explore various categories of adjectives, provide numerous examples, and offer practical exercises to solidify your understanding. This comprehensive guide ensures you can confidently and accurately describe the men in your life, both real and fictional.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Adjectives
- Structural Breakdown of Adjectives
- Types of Adjectives
- Examples of Adjectives for Guys
- Usage Rules for Adjectives
- Common Mistakes with Adjectives
- Practice Exercises
- Advanced Topics in Adjectives
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Definition of Adjectives
An adjective is a word that modifies or describes a noun or pronoun. It provides more information about the noun, adding detail and specificity. Adjectives answer questions like “What kind?”, “Which one?”, “How many?”, or “How much?” They are essential for creating vivid and descriptive language.
Classification: Adjectives are primarily classified based on their function and the type of information they convey. This classification includes descriptive, quantitative, demonstrative, possessive, interrogative, proper, and compound adjectives. Each type serves a unique purpose in modifying nouns and pronouns.
Function: The primary function of an adjective is to provide additional details about a noun. This can include physical characteristics, personality traits, or any other attribute that helps to define the noun more precisely. Adjectives enrich language and allow for more nuanced communication.
Contexts: Adjectives are used in a wide range of contexts, from everyday conversation to formal writing. They are crucial in descriptive writing, storytelling, and any form of communication where detail and clarity are important. The appropriate use of adjectives can significantly enhance the impact and effectiveness of your message.
Structural Breakdown of Adjectives
Adjectives typically precede the noun they modify (e.g., “a tall man”) but can also follow a linking verb (e.g., “He is tall“). Understanding this placement is crucial for constructing grammatically correct sentences.
Attributive Adjectives: These adjectives come before the noun they modify. For example, in the phrase “a strong leader,” the adjective “strong” is attributive because it directly precedes the noun “leader.”
Predicative Adjectives: These adjectives follow a linking verb and describe the subject of the sentence. In the sentence “He is intelligent,” the adjective “intelligent” is predicative because it follows the linking verb “is” and describes the subject “He.” Common linking verbs include be (is, are, was, were, been, being), seem, become, appear, look, sound, smell, taste, and feel.
Order of Adjectives: When using multiple adjectives, there’s a general order to follow: opinion, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, and purpose. For example, “a beautiful (opinion) large (size) old (age) square (shape) red (color) Italian (origin) wooden (material) table.” This order ensures clarity and natural-sounding language.
Coordinate Adjectives: These are adjectives of equal rank that modify the same noun. They are separated by a comma or the word “and.” For example, “a smart, capable man” or “a kind and generous person.” Coordinate adjectives can be rearranged without changing the meaning of the sentence.
Types of Adjectives
Adjectives can be categorized into several types based on their function and the kind of information they provide.
Descriptive Adjectives
Descriptive adjectives, also known as qualitative adjectives, describe the qualities or characteristics of a noun. They answer the question “What kind?” These are the most common types of adjectives.
Examples include: handsome, brave, intelligent, kind, athletic, charming, witty, serious, confident, ambitious.
Quantitative Adjectives
Quantitative adjectives indicate the quantity or amount of the noun. They answer the question “How many?” or “How much?”
Examples include: few, many, several, some, all, no, one, two, three. For example, “Several strong men participated in the contest.”
Demonstrative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives point out specific nouns. They include this, that, these, and those. They answer the question “Which one(s)?”
Examples include: “This tall man is my brother.” “Those muscular guys are training for the competition.”
Possessive Adjectives
Possessive adjectives show ownership or possession. They include my, your, his, her, its, our, and their. They indicate who or what owns the noun.
Examples include: “His strong will helped him overcome challenges.” “Their athletic prowess was evident in the game.”
Interrogative Adjectives
Interrogative adjectives are used to ask questions about nouns. They include what, which, and whose. They are always followed by a noun.
Examples include: “Which tall man is the coach?” “What kind of personality does he have?”
Proper Adjectives
Proper adjectives are formed from proper nouns. They describe nouns by indicating their origin or association with a specific place, person, or thing. They are always capitalized.
Examples include: American (from America), Italian (from Italy), Shakespearean (from Shakespeare). For example, “He has an Italian charm.”
Compound Adjectives
Compound adjectives are formed by combining two or more words, often joined by a hyphen. They act as a single adjective to describe a noun.
Examples include: well-known, good-looking, hard-working, open-minded. For example, “He is a hard-working man.”
Examples of Adjectives for Guys
This section provides a comprehensive list of adjectives commonly used to describe men, categorized by different aspects such as appearance, personality, skills, and character.
Appearance
Adjectives describing a man’s appearance can range from general terms to more specific features.
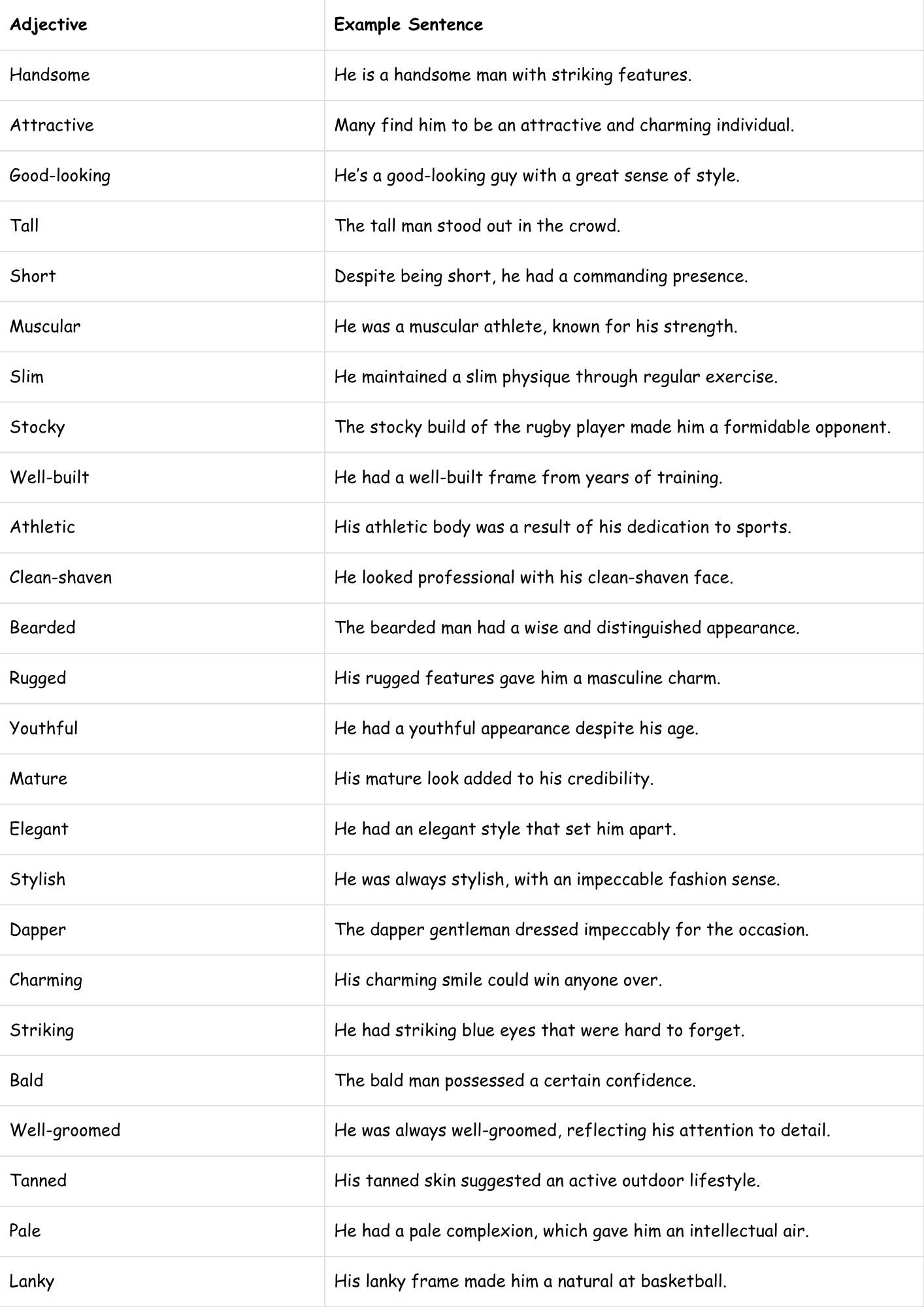
The following table provides a wide selection of adjectives to describe a man’s physical appearance, offering examples of how they can be used in sentences.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Handsome | He is a handsome man with striking features. |
| Attractive | Many find him to be an attractive and charming individual. |
| Good-looking | He’s a good-looking guy with a great sense of style. |
| Tall | The tall man stood out in the crowd. |
| Short | Despite being short, he had a commanding presence. |
| Muscular | He was a muscular athlete, known for his strength. |
| Slim | He maintained a slim physique through regular exercise. |
| Stocky | The stocky build of the rugby player made him a formidable opponent. |
| Well-built | He had a well-built frame from years of training. |
| Athletic | His athletic body was a result of his dedication to sports. |
| Clean-shaven | He looked professional with his clean-shaven face. |
| Bearded | The bearded man had a wise and distinguished appearance. |
| Rugged | His rugged features gave him a masculine charm. |
| Youthful | He had a youthful appearance despite his age. |
| Mature | His mature look added to his credibility. |
| Elegant | He had an elegant style that set him apart. |
| Stylish | He was always stylish, with an impeccable fashion sense. |
| Dapper | The dapper gentleman dressed impeccably for the occasion. |
| Charming | His charming smile could win anyone over. |
| Striking | He had striking blue eyes that were hard to forget. |
| Bald | The bald man possessed a certain confidence. |
| Well-groomed | He was always well-groomed, reflecting his attention to detail. |
| Tanned | His tanned skin suggested an active outdoor lifestyle. |
| Pale | He had a pale complexion, which gave him an intellectual air. |
| Lanky | His lanky frame made him a natural at basketball. |
Personality
Describing a man’s personality involves using adjectives that capture his character traits and behaviors.
Here’s a table full of adjectives that describe personality traits, accompanied by illustrative sentences to demonstrate their usage.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Intelligent | He is an intelligent man with a sharp mind. |
| Brave | He showed himself to be a brave leader in times of crisis. |
| Kind | He is a kind soul, always willing to help others. |
| Generous | His generous nature made him a beloved member of the community. |
| Loyal | He is a loyal friend, always there for support. |
| Honest | He is known for being an honest and trustworthy individual. |
| Ambitious | He is an ambitious man with clear goals and aspirations. |
| Confident | He is a confident speaker, comfortable in front of any audience. |
| Humble | Despite his success, he remains humble and grounded. |
| Witty | He is a witty conversationalist, always making people laugh. |
| Charming | He has a charming personality that attracts people to him. |
| Serious | He is a serious professional, dedicated to his work. |
| Easygoing | He has an easygoing attitude, making him a pleasure to be around. |
| Optimistic | He is an optimistic person, always seeing the best in situations. |
| Pessimistic | He tends to be pessimistic, often focusing on potential problems. |
| Reserved | He is reserved and doesn’t easily share his feelings. |
| Outgoing | He is an outgoing individual, always eager to meet new people. |
| Patient | He is a patient teacher, understanding and supportive. |
| Impatient | He can be impatient when things don’t move quickly. |
| Courageous | He is courageous in the face of adversity. |
| Determined | He is a determined individual, never giving up on his goals. |
| Compassionate | He is compassionate and cares deeply about others. |
| Independent | He is an independent thinker, relying on his own judgment. |
| Adaptable | He is adaptable and can easily adjust to new situations. |
| Resourceful | He is a resourceful problem solver, finding creative solutions. |
Skills and Abilities
Adjectives that describe a man’s skills and abilities highlight his talents and capabilities.
This table offers examples of adjectives used to describe skills and abilities, with accompanying sentences to illustrate their usage in context.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Skilled | He is a skilled craftsman, known for his attention to detail. |
| Talented | He is a talented musician, captivating audiences with his performances. |
| Capable | He is a capable leader, trusted by his team. |
| Proficient | He is proficient in multiple languages, making him an asset in international business. |
| Adept | He is adept at solving complex problems, earning him respect in his field. |
| Experienced | He is an experienced engineer, having worked on numerous projects. |
| Knowledgeable | He is a knowledgeable historian, well-versed in various eras. |
| Creative | He is a creative writer, known for his originality and imagination. |
| Innovative | He is an innovative thinker, always coming up with new ideas. |
| Artistic | He is an artistic photographer, capturing stunning images. |
| Technical | He has technical expertise in software development. |
| Analytical | He has analytical skills that are invaluable for data analysis. |
| Strategic | He is a strategic planner, skilled at long-term thinking. |
| Efficient | He is an efficient worker, always meeting deadlines. |
| Organized | He is highly organized, keeping everything in order. |
| Disciplined | He is a disciplined athlete, committed to his training regimen. |
| Athletic | He is an athletic runner, competing in marathons. |
| Musical | He is a musical prodigy, mastering multiple instruments. |
| Linguistic | He has linguistic abilities that allow him to learn languages quickly. |
| Mechanical | He has a mechanical aptitude for fixing engines and machines. |
| Leadership | He demonstrates leadership qualities that inspire his team. |
| Communication | He has excellent communication skills, making him an effective presenter. |
| Negotiation | He is skilled in negotiation, securing favorable deals. |
| Problem-solving | He has strong problem-solving abilities, finding solutions under pressure. |
| Decision-making | He is decisive in decision-making, even in challenging situations. |
Character
Describing a man’s character involves adjectives that reflect his moral and ethical qualities.
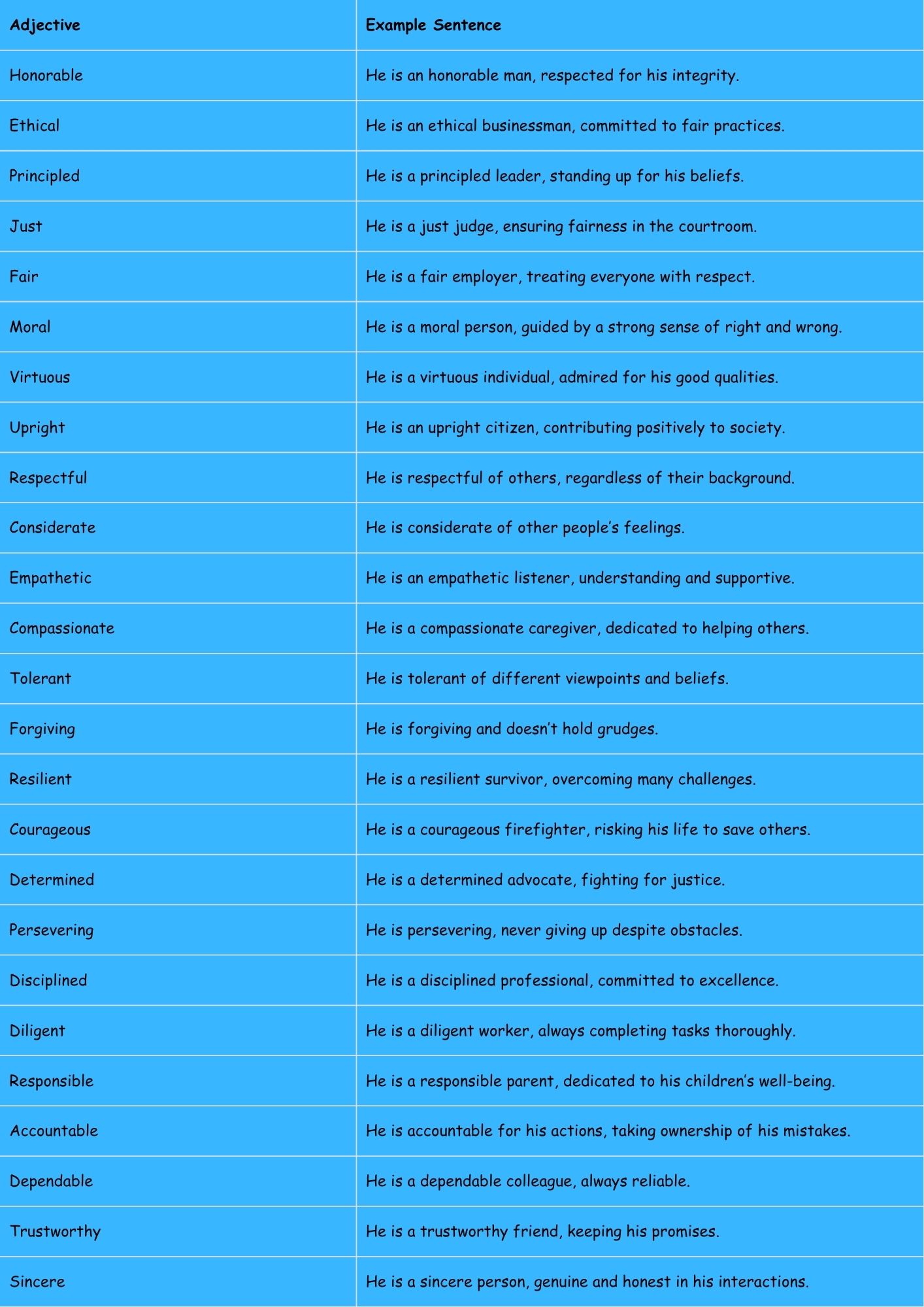
The following table provides a range of adjectives to describe a man’s character, along with sentences to illustrate their use.
| Adjective | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| Honorable | He is an honorable man, respected for his integrity. |
| Ethical | He is an ethical businessman, committed to fair practices. |
| Principled | He is a principled leader, standing up for his beliefs. |
| Just | He is a just judge, ensuring fairness in the courtroom. |
| Fair | He is a fair employer, treating everyone with respect. |
| Moral | He is a moral person, guided by a strong sense of right and wrong. |
| Virtuous | He is a virtuous individual, admired for his good qualities. |
| Upright | He is an upright citizen, contributing positively to society. |
| Respectful | He is respectful of others, regardless of their background. |
| Considerate | He is considerate of other people’s feelings. |
| Empathetic | He is an empathetic listener, understanding and supportive. |
| Compassionate | He is a compassionate caregiver, dedicated to helping others. |
| Tolerant | He is tolerant of different viewpoints and beliefs. |
| Forgiving | He is forgiving and doesn’t hold grudges. |
| Resilient | He is a resilient survivor, overcoming many challenges. |
| Courageous | He is a courageous firefighter, risking his life to save others. |
| Determined | He is a determined advocate, fighting for justice. |
| Persevering | He is persevering, never giving up despite obstacles. |
| Disciplined | He is a disciplined professional, committed to excellence. |
| Diligent | He is a diligent worker, always completing tasks thoroughly. |
| Responsible | He is a responsible parent, dedicated to his children’s well-being. |
| Accountable | He is accountable for his actions, taking ownership of his mistakes. |
| Dependable | He is a dependable colleague, always reliable. |
| Trustworthy | He is a trustworthy friend, keeping his promises. |
| Sincere | He is a sincere person, genuine and honest in his interactions. |
Usage Rules for Adjectives
Understanding the rules for using adjectives is crucial for clear and effective communication.
Adjective Placement: Adjectives usually come before the noun they modify. However, they can also follow linking verbs. For example:
- Correct: “He is a talented musician.”
- Correct: “He seems talented.”
Order of Adjectives: When using multiple adjectives, follow the general order: opinion, size, age, shape, color, origin, material, purpose. For example:
- Correct: “a beautiful large old square red Italian wooden table”
Coordinate Adjectives: Use a comma between coordinate adjectives, which are adjectives of equal rank that modify the same noun. For example:
- Correct: “a smart, capable man”
Comparative and Superlative Forms: Use comparative forms (-er or more) to compare two things and superlative forms (-est or most) to compare three or more things. For example:
- Comparative: “He is stronger than his brother.”
- Superlative: “He is the strongest man in the world.”
Articles with Adjectives: Use articles (a, an, the) appropriately with adjectives. “A” and “an” are used before singular countable nouns, while “the” is used for specific or unique nouns. For example:
- Correct: “He is a talented musician.”
- Correct: “He is the best musician in the orchestra.”
Exceptions and Special Cases: Some adjectives have irregular comparative and superlative forms (e.g., good, better, best; bad, worse, worst). Some adjectives are non-gradable, meaning they cannot be used in comparative or superlative forms (e.g., unique, perfect). For example:
- Correct: “He is better at singing than I am.”
- Incorrect: “He is more unique than anyone else.” (Unique already means one of a kind)
Common Mistakes with Adjectives
Avoiding common mistakes with adjectives can significantly improve your writing and speaking skills.
The following table highlights common mistakes with adjectives, providing both incorrect and correct examples for clarity.
| Mistake | Incorrect Example | Correct Example |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Adjective Form | He is the most tallest man in the room. | He is the tallest man in the room. |
| Misplaced Adjective | The man tall is my brother. | The tall man is my brother. |
| Incorrect Use of Articles | He is a best player. | He is the best player. |
| Incorrect Comparative/Superlative | He is more better than me. | He is better than me. |
| Using Adjective as Adverb | He runs quick. | He runs quickly. |
| Double Negatives | He is not unkind. (Intended meaning: He is kind) | He is kind. |
| Incorrect Order of Adjectives | A red big car. | A big red car. |
| Using Non-Gradable Adjectives Comparatively | This solution is more perfect than that one. | This solution is perfect. |
| Confusing Adjectives with Similar Meanings | He is a economic man. | He is an economical man. |
| Using Too Many Adjectives | He is a handsome, intelligent, kind, charming, witty man. | He is a handsome and intelligent man. |
Practice Exercises
These exercises will help you practice using adjectives correctly and effectively.
Exercise 1: Identifying Adjectives
Identify the adjectives in the following sentences.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. The brave soldier received an award. | brave |
| 2. He is a talented artist. | talented |
| 3. The old house stood on the hill. | old |
| 4. She wore a red dress. | red |
| 5. The intelligent student aced the test. | intelligent |
| 6. He is a kind and generous man. | kind, generous |
| 7. The strong wind blew through the trees. | strong |
| 8. She has a charming personality. | charming |
| 9. The new car is very fast. | new, fast |
| 10. He is an ambitious entrepreneur. | ambitious |
Exercise 2: Using Descriptive Adjectives
Fill in the blanks with appropriate descriptive adjectives.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. He is a __________ man with a __________ smile. | handsome, charming |
| 2. The __________ athlete won the __________ race. | athletic, difficult |
| 3. She is a __________ and __________ teacher. | patient, kind |
| 4. He lives in a __________ house with a __________ garden. | large, beautiful |
| 5. The __________ student asked a __________ question. | curious, insightful |
| 6. The __________ dog barked at the __________ stranger. | aggressive, suspicious |
| 7. He wore a __________ coat on a __________ day. | warm, cold |
| 8. She has a __________ voice and a __________ laugh. | melodious, contagious |
| 9. The __________ chef prepared a __________ meal. | skilled, delicious |
| 10. He is a __________ leader with a __________ vision. | strong, clear |
Exercise 3: Correcting Adjective Errors
Identify and correct the adjective errors in the following sentences.
| Question | Corrected Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. He is the most tallest player on the team. | He is the tallest player on the team. |
| 2. She is more better than me at tennis. | She is better than me at tennis. |
| 3. He runs very quick. | He runs very quickly. |
| 4. This is a red big car. | This is a big red car. |
| 5. He is a economic man. | He is an economical man. |
| 6. She is the most unique person I know. | She is a unique person I know. |
| 7. The man tall is my brother. | The tall man is my brother. |
| 8. He is not unkind. | He is kind. |
| 9. She has a beautiful blue eyes. | She has beautiful blue eyes. |
| 10. He is a best student in the class. | He is the best student in the class. |
Advanced Topics in Adjectives
For advanced learners, understanding more complex aspects of adjectives can further refine their language skills.
Gradable and Non-Gradable Adjectives: Gradable adjectives can be modified by adverbs of degree (e.g., very, extremely), while non-gradable adjectives cannot (e.g., unique, perfect). Understanding this distinction is crucial for precise language use.
Attributive vs. Predicative Adjectives in Depth: While attributive adjectives directly precede the noun and predicative adjectives follow a linking verb, some adjectives can only be used in one form. For example, “elder” is typically used attributively (“my elder brother”), while “afraid” is typically used predicatively (“He is afraid”).
Subjective vs. Objective Adjectives: Subjective adjectives express opinions or judgments (e.g., beautiful, interesting), while objective adjectives describe factual qualities (e.g., tall, red). Recognizing this difference can enhance your writing’s clarity and persuasive power.
Using Adjectives to Create Tone and Mood: The choice of adjectives can significantly impact the tone and mood of a piece of writing. For example, using words like “gloomy” and “desolate” creates a somber mood, while words like “vibrant” and “joyful” create a cheerful atmosphere. This is particularly relevant in creative writing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about using adjectives.
Q1: What is the difference between an adjective and an adverb?
A: An adjective modifies a noun or pronoun, while an adverb modifies a verb, adjective, or another adverb. Adjectives answer questions like “What kind?” or “Which one?” while adverbs answer questions like “How?”, “When?”, “Where?”, or “To what extent?”. For example, “He is a fast runner” (adjective) vs. “He runs fast” (adverb).
Q2: Can a noun be used as an adjective?
A: Yes, a noun can be used as an adjective, also known as a noun adjunct or attributive noun. In this case, the noun modifies another noun. For example, “a computer programmer” (computer modifies programmer).
Q3: How do I know the correct order of adjectives when using multiple adjectives?
A: The general order of adjectives is opinion, size, age, shape, color, origin, material
, and purpose. While this is a helpful guideline, it’s also important to consider what sounds most natural in the context of your sentence. If the order sounds awkward, try rearranging the adjectives to improve clarity and flow.
Q4: Are there any adjectives that should be avoided when describing someone?
A: While there are no strictly “forbidden” adjectives, it’s important to be mindful of the connotations and potential impact of your words. Avoid adjectives that are offensive, discriminatory, or perpetuate harmful stereotypes. Always strive to use language that is respectful and considerate.
Conclusion
Mastering the use of adjectives is essential for effective and descriptive communication. By understanding the different types of adjectives, their usage rules, and common mistakes to avoid, you can significantly enhance your ability to describe men accurately and vividly. Whether you are writing creatively, improving your language skills, or simply looking to expand your vocabulary, this comprehensive guide provides the knowledge and resources you need. Continue practicing the exercises and applying these concepts in your writing and speech to further refine your skills.



