Understanding how to use adjectives to describe networks is crucial for anyone involved in technology, business, or social sciences. Adjectives help us specify the characteristics, qualities, and attributes of various network types, enabling clearer communication and more precise analysis. This article provides a detailed exploration of adjectives used to describe networks, covering their definitions, usage rules, common mistakes, and practical examples. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply interested in expanding your vocabulary, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to describe networks effectively and accurately.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Definition of Adjectives for Networks
- Structural Breakdown
- Types and Categories of Adjectives for Networks
- Examples of Adjectives for Networks
- Usage Rules for Adjectives Describing Networks
- Common Mistakes When Using Adjectives for Networks
- Practice Exercises
- Advanced Topics
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Definition of Adjectives for Networks
Adjectives, in general, are words that modify or describe nouns, providing more information about them. When used in the context of networks, adjectives help to specify the characteristics, qualities, or attributes of a particular network. A network, in this context, refers to a group of interconnected devices, systems, or people. The function of adjectives in describing networks is to provide a clearer and more detailed understanding of the network’s nature, capabilities, and limitations. This could involve describing the network’s size (e.g., large, small), its performance (e.g., fast, efficient), its security features (e.g., secure, vulnerable), or its topology (e.g., star, mesh). Adjectives are essential for effective communication and precise analysis when discussing networks in various contexts.
The classification of adjectives for networks can be based on the aspect they describe. For example, some adjectives relate to the physical structure of the network, while others describe its functional properties. Understanding this classification helps in choosing the most appropriate adjective for a given situation. The context in which these adjectives are used can range from technical documentation and academic papers to everyday conversations about technology. Therefore, a broad understanding of these adjectives is beneficial for anyone who interacts with network-related concepts.
Structural Breakdown
The structural use of adjectives in describing networks follows standard English grammar rules. Typically, an adjective is placed before the noun it modifies. For example, in the phrase “a secure network,” the adjective “secure” precedes the noun “network.” However, adjectives can also be used after linking verbs such as is, are, was, and were. For example, “The network is reliable.” Here, “reliable” follows the linking verb “is” and describes the network.
Adjectives can also be modified by adverbs to provide an even more precise description. For instance, in the phrase “a highly efficient network,” the adverb “highly” modifies the adjective “efficient,” indicating a greater degree of efficiency. The order of adjectives is also important when using multiple adjectives to describe a network. While there isn’t a strict rule, it’s generally recommended to follow the order of opinion, size, physical quality, shape, age, color, origin, and material. For example, “a modern, large, wired network” sounds more natural than “a wired, large, modern network.” Understanding these structural elements helps in constructing grammatically correct and meaningful descriptions of networks.
Types and Categories of Adjectives for Networks
Adjectives for networks can be categorized based on the specific aspect of the network they describe. This categorization helps in selecting the most appropriate adjective for a given context. Here are some key categories:
Size-Related Adjectives
These adjectives describe the scale or extent of the network. Examples include: small, large, extensive, widespread, global, local, regional, campus-wide, metropolitan, and personal. These adjectives help to understand the network’s physical or logical reach.
Performance-Related Adjectives
These adjectives describe the speed, efficiency, and capacity of the network. Examples include: fast, slow, efficient, high-bandwidth, low-latency, responsive, scalable, reliable, stable, and robust. These adjectives are crucial for evaluating the network’s operational capabilities.
Security-Related Adjectives
These adjectives describe the level of protection and vulnerability of the network. Examples include: secure, vulnerable, protected, encrypted, firewalled, authenticated, private, public, trusted, and unsecured. These adjectives are essential for assessing the network’s security posture.
Topology-Related Adjectives
These adjectives describe the physical or logical arrangement of the network. Examples include: star, mesh, ring, bus, tree, hybrid, distributed, centralized, decentralized, and point-to-point. These adjectives help to understand the network’s structure and organization.
Purpose-Related Adjectives
These adjectives describe the intended use or function of the network. Examples include: business, social, educational, research, entertainment, communication, industrial, commercial, private, and public. These adjectives provide context about the network’s primary application.
Technology-Related Adjectives
These adjectives describe the technologies used to build and operate the network. Examples include: wired, wireless, Ethernet, fiber-optic, cellular, satellite, cloud-based, virtual, software-defined, and legacy. These adjectives specify the technical underpinnings of the network.
Reliability-Related Adjectives
These adjectives describe the consistency and dependability of the network. Examples include: reliable, unreliable, stable, unstable, resilient, redundant, fault-tolerant, consistent, dependable, and robust. These adjectives are vital for evaluating the network’s uptime and performance consistency.
Examples of Adjectives for Networks
The following are examples of adjectives used to describe networks, categorized by the types discussed above. These examples illustrate how adjectives can be used in sentences to provide specific details about different networks.
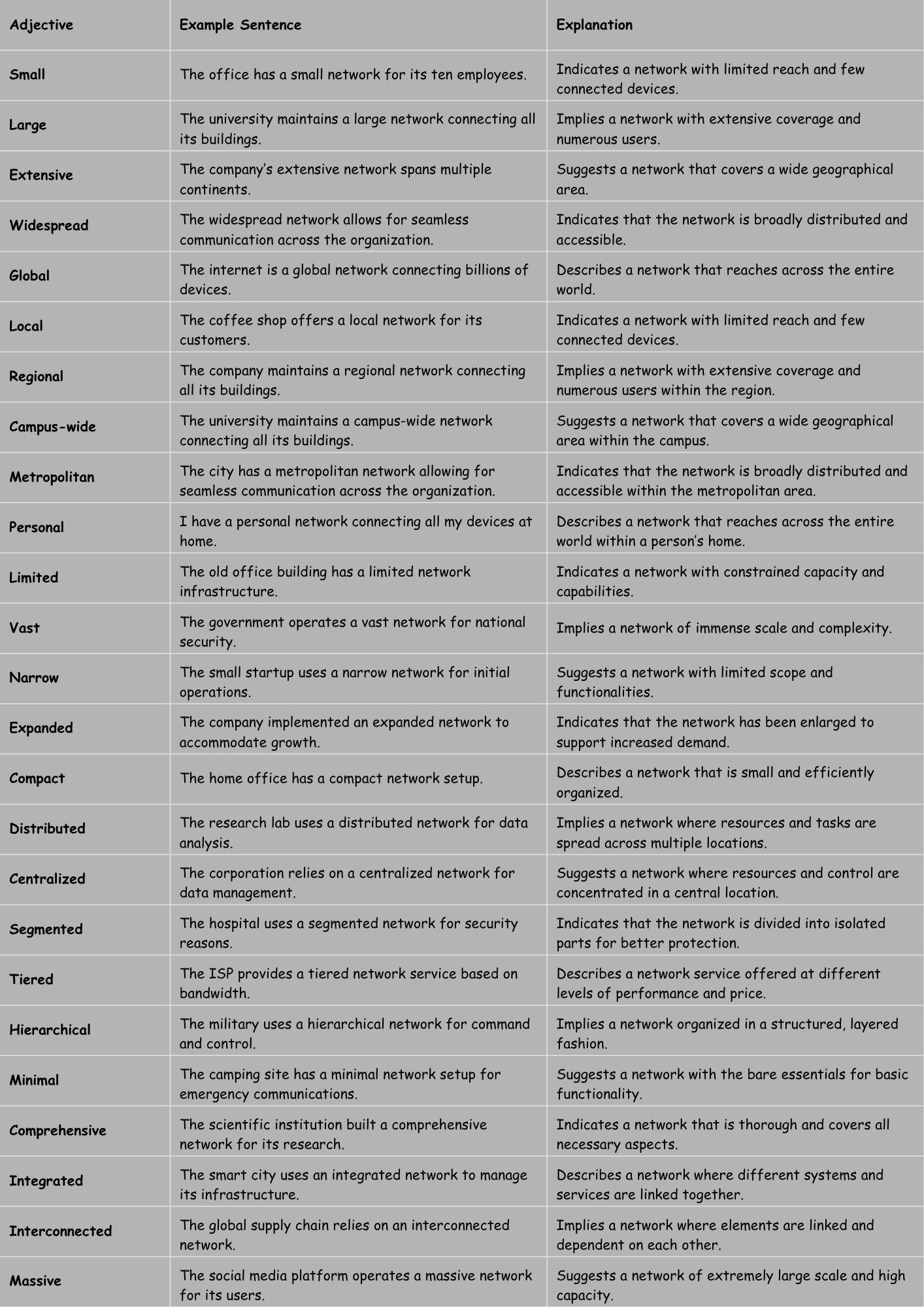
Size-Related Examples
This table illustrates the use of size-related adjectives in describing different network scenarios. From personal networks to global infrastructures, the adjectives provide a clear sense of scale.
| Adjective | Example Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Small | The office has a small network for its ten employees. | Indicates a network with limited reach and few connected devices. |
| Large | The university maintains a large network connecting all its buildings. | Implies a network with extensive coverage and numerous users. |
| Extensive | The company’s extensive network spans multiple continents. | Suggests a network that covers a wide geographical area. |
| Widespread | The widespread network allows for seamless communication across the organization. | Indicates that the network is broadly distributed and accessible. |
| Global | The internet is a global network connecting billions of devices. | Describes a network that reaches across the entire world. |
| Local | The coffee shop offers a local network for its customers. | Indicates a network with limited reach and few connected devices. |
| Regional | The company maintains a regional network connecting all its buildings. | Implies a network with extensive coverage and numerous users within the region. |
| Campus-wide | The university maintains a campus-wide network connecting all its buildings. | Suggests a network that covers a wide geographical area within the campus. |
| Metropolitan | The city has a metropolitan network allowing for seamless communication across the organization. | Indicates that the network is broadly distributed and accessible within the metropolitan area. |
| Personal | I have a personal network connecting all my devices at home. | Describes a network that reaches across the entire world within a person’s home. |
| Limited | The old office building has a limited network infrastructure. | Indicates a network with constrained capacity and capabilities. |
| Vast | The government operates a vast network for national security. | Implies a network of immense scale and complexity. |
| Narrow | The small startup uses a narrow network for initial operations. | Suggests a network with limited scope and functionalities. |
| Expanded | The company implemented an expanded network to accommodate growth. | Indicates that the network has been enlarged to support increased demand. |
| Compact | The home office has a compact network setup. | Describes a network that is small and efficiently organized. |
| Distributed | The research lab uses a distributed network for data analysis. | Implies a network where resources and tasks are spread across multiple locations. |
| Centralized | The corporation relies on a centralized network for data management. | Suggests a network where resources and control are concentrated in a central location. |
| Segmented | The hospital uses a segmented network for security reasons. | Indicates that the network is divided into isolated parts for better protection. |
| Tiered | The ISP provides a tiered network service based on bandwidth. | Describes a network service offered at different levels of performance and price. |
| Hierarchical | The military uses a hierarchical network for command and control. | Implies a network organized in a structured, layered fashion. |
| Minimal | The camping site has a minimal network setup for emergency communications. | Suggests a network with the bare essentials for basic functionality. |
| Comprehensive | The scientific institution built a comprehensive network for its research. | Indicates a network that is thorough and covers all necessary aspects. |
| Integrated | The smart city uses an integrated network to manage its infrastructure. | Describes a network where different systems and services are linked together. |
| Interconnected | The global supply chain relies on an interconnected network. | Implies a network where elements are linked and dependent on each other. |
| Massive | The social media platform operates a massive network for its users. | Suggests a network of extremely large scale and high capacity. |
Performance-Related Examples
This table provides examples of performance-related adjectives, highlighting the speed, efficiency, and reliability of different networks. These adjectives are important for evaluating network quality and suitability for various tasks.
| Adjective | Example Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Fast | The company upgraded to a fast network to improve productivity. | Indicates a network with high data transfer speeds. |
| Slow | The old infrastructure resulted in a slow network. | Implies a network with low data transfer speeds. |
| Efficient | The efficient network minimizes data loss and maximizes throughput. | Suggests a network that operates with optimal resource utilization. |
| High-bandwidth | The streaming service requires a high-bandwidth network. | Indicates a network capable of handling large volumes of data. |
| Low-latency | Gamers prefer a low-latency network for real-time responsiveness. | Describes a network with minimal delay in data transmission. |
| Responsive | A responsive network is crucial for time-sensitive applications. | Indicates a network that reacts quickly to user requests. |
| Scalable | The scalable network can adapt to increasing demands. | Suggests a network that can easily expand to accommodate more users or data. |
| Reliable | A reliable network is essential for business continuity. | Implies a network that consistently performs as expected. |
| Stable | The stable network ensures uninterrupted service. | Indicates a network that is resistant to disruptions and outages. |
| Robust | The robust network can withstand heavy traffic and attacks. | Describes a network that is strong and resilient under pressure. |
| Optimized | The optimized network delivers peak performance. | Suggests a network that has been fine-tuned for maximum efficiency. |
| Uncongested | An uncongested network ensures smooth data flow. | Indicates a network with minimal traffic bottlenecks. |
| Streamlined | The streamlined network simplifies data management. | Describes a network that is well-organized and efficient. |
| Accelerated | The accelerated network speeds up critical processes. | Suggests a network that has been enhanced for faster performance. |
| Consistent | The consistent network provides reliable service at all times. | Indicates a network that maintains a stable level of performance. |
| High-performance | The data center requires a high-performance network. | Describes a network designed for demanding tasks and applications. |
| Low-power | The IoT devices use a low-power network to conserve energy. | Suggests a network designed for minimal energy consumption. |
| Adaptive | The adaptive network adjusts to changing conditions. | Indicates a network that can automatically respond to variations in demand. |
| Agile | The agile network supports rapid deployment and changes. | Describes a network that is flexible and responsive to new requirements. |
| Dynamic | The dynamic network optimizes resource allocation in real-time. | Suggests a network that is constantly adjusting to improve performance. |
| Overloaded | The overloaded network had issues transmitting the data. | Implies a network with too much traffic. |
| Snappy | The new and improved network is snappy and allows for faster speeds. | Indicates a network that reacts quickly to user requests. |
| Dependable | The dependable network supports rapid deployment and changes. | Describes a network that is flexible and responsive to new requirements. |
| Expedient | The expedient network optimizes resource allocation in real-time. | Suggests a network that is constantly adjusting to improve performance. |
| Uninterrupted | The uninterrupted network ensures smooth data flow. | Indicates a network with minimal traffic bottlenecks. |
Security-Related Examples
This table illustrates the use of security-related adjectives to describe the protective measures and vulnerabilities of different networks. These adjectives are crucial for understanding and assessing network security risks.
| Adjective | Example Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Secure | The bank uses a secure network to protect customer data. | Indicates a network with strong security measures. |
| Vulnerable | The outdated system made the network vulnerable to attacks. | Implies a network with weaknesses that can be exploited. |
| Protected | The protected network is shielded from external threats. | Suggests a network with safeguards in place to prevent breaches. |
| Encrypted | The encrypted network ensures data privacy. | Indicates that data is encoded to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Firewalled | The firewalled network blocks unauthorized connections. | Describes a network with a firewall to control traffic. |
| Authenticated | The authenticated network requires users to verify their identity. | Suggests a network that verifies user credentials before granting access. |
| Private | The company operates a private network for internal communications. | Indicates a network restricted to authorized users. |
| Public | The library offers a public network for visitors. | Implies a network accessible to anyone. |
| Trusted | The trusted network is used for sensitive transactions. | Suggests a network with a high level of confidence in its security. |
| Unsecured | The unsecured network is susceptible to hacking. | Describes a network without adequate security measures. |
| Monitored | The monitored network is constantly watched for threats. | Indicates a network under surveillance for security breaches. |
| Isolated | The isolated network prevents the spread of malware. | Suggests a network separated from other networks to limit exposure. |
| Hardened | The hardened network has been fortified against attacks. | Describes a network with strengthened security defenses. |
| Resilient | The resilient network can recover from security incidents. | Indicates a network that can quickly restore operations after an attack. |
| Segmented | The segmented network limits the impact of breaches. | Suggests a network divided into isolated sections for better security. |
| Compliant | The compliant network meets industry security standards. | Describes a network that adheres to regulatory requirements. |
| Audited | The audited network undergoes regular security checks. | Indicates a network that is periodically assessed for vulnerabilities. |
| Protected | The protected network is shielded from external threats. | Suggests a network with safeguards in place to prevent breaches. |
| Filtered | The filtered network blocks malicious content. | Describes a network that screens incoming and outgoing traffic. |
| Guarded | The guarded network is closely defended against intrusions. | Indicates a network under strict security surveillance. |
| Defended | The defended network is safe from attacks. | Implies a network with weaknesses that can be exploited. |
| Impenetrable | The impenetrable network is shielded from external threats. | Suggests a network with safeguards in place to prevent breaches. |
| Watched | The watched network ensures data privacy. | Indicates that data is encoded to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Guarded | The guarded network blocks unauthorized connections. | Describes a network with a firewall to control traffic. |
| Restricted | The restricted network requires users to verify their identity. | Suggests a network that verifies user credentials before granting access. |
Topology-Related Examples
| Adjective | Example Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Star | The office uses a star network topology for easy management. | Describes a network where all devices connect to a central hub. |
| Mesh | The complex system uses a mesh network for redundancy. | Indicates a network where devices are interconnected with multiple paths. |
| Ring | The older system used a ring network, which is now outdated. | Describes a network where devices are connected in a circular fashion. |
| Bus | The small setup relied on a bus network for simplicity. | Indicates a network where devices share a single communication line. |
| Tree | The large organization uses a tree network for hierarchical structure. | Describes a network with a hierarchical structure resembling a tree. |
| Hybrid | The modern setup uses a hybrid network for flexibility. | Indicates a network that combines multiple topologies. |
| Distributed | The research lab employs a distributed network for data processing. | Describes a network where resources are spread across multiple locations. |
| Centralized | The corporation operates a centralized network for data management. | Indicates a network where resources are concentrated in a central location. |
| Decentralized | The blockchain system uses a decentralized network for security. | Describes a network where control is distributed among participants. |
| Point-to-point | The direct connection uses a point-to-point network for simplicity. | Indicates a network with a direct link between two devices. |
Purpose-Related Examples
| Adjective | Example Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Business | The company relies on a business network for its operations. | Describes a network used for commercial activities. |
| Social | The platform provides a social network for connecting people. | Indicates a network used for social interaction and communication. |
| Educational | The school uses an educational network for learning resources. | Describes a network used for academic purposes. |
| Research | The university maintains a research network for data analysis. | Indicates a network used for scientific investigation. |
| Entertainment | The streaming service uses an entertainment network for content delivery. | Describes a network used for providing media and leisure activities. |
| Communication | The office uses a communication network for internal messaging. | Indicates a network used for transmitting information. |
| Industrial | The factory utilizes an industrial network for automation. | Describes a network used for managing manufacturing processes. |
| Commercial | The retailer uses a commercial network for transactions. | Indicates a network used for buying and selling goods or services. |
| Private | The home has a private network for personal use. | Describes a network used exclusively by the household. |
| Public | The park offers a public network for visitors. | Indicates a network accessible to the general public. |
Technology-Related Examples
| Adjective | Example Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Wired | The office uses a wired network for reliable connections. | Describes a network that uses physical cables for data transmission. |
| Wireless | The café provides a wireless network for customers. | Indicates a network that uses radio waves for data transmission. |
| Ethernet | The lab uses an Ethernet network for high-speed communication. | Describes a network that uses the Ethernet protocol. |
| Fiber-optic | The data center utilizes a fiber-optic network for fast data transfer. | Indicates a network that uses optical fibers for data transmission. |
| Cellular | The mobile device connects to a cellular network for internet access. | Describes a network that uses cell towers for data transmission. |
| Satellite | The remote location uses a satellite network for communication. | Indicates a network that uses satellites for data transmission. |
| Cloud-based | The company uses a cloud-based network for data storage. | Describes a network that relies on cloud computing services. |
| Virtual | The system operates on a virtual network for flexibility. | Indicates a network created using virtualization technology. |
| Software-defined | The modern infrastructure uses a software-defined network for control. | Describes a network controlled by software. |
| Legacy | The older system relies on a legacy network, which is being phased out. | Indicates an outdated network technology. |
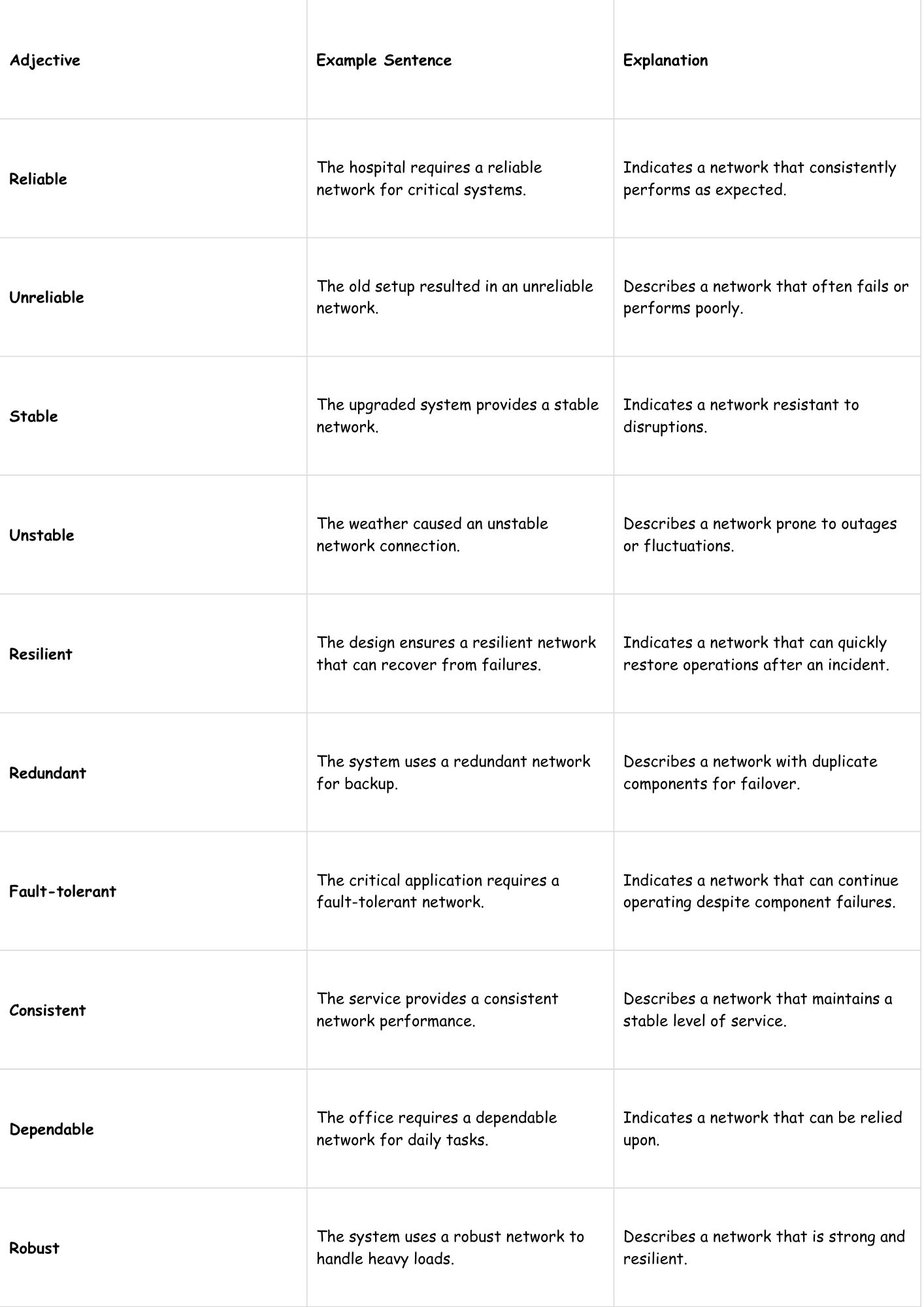
Reliability-Related Examples
| Adjective | Example Sentence | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Reliable | The hospital requires a reliable network for critical systems. | Indicates a network that consistently performs as expected. |
| Unreliable | The old setup resulted in an unreliable network. | Describes a network that often fails or performs poorly. |
| Stable | The upgraded system provides a stable network. | Indicates a network resistant to disruptions. |
| Unstable | The weather caused an unstable network connection. | Describes a network prone to outages or fluctuations. |
| Resilient | The design ensures a resilient network that can recover from failures. | Indicates a network that can quickly restore operations after an incident. |
| Redundant | The system uses a redundant network for backup. | Describes a network with duplicate components for failover. |
| Fault-tolerant | The critical application requires a fault-tolerant network. | Indicates a network that can continue operating despite component failures. |
| Consistent | The service provides a consistent network performance. | Describes a network that maintains a stable level of service. |
| Dependable | The office requires a dependable network for daily tasks. | Indicates a network that can be relied upon. |
| Robust | The system uses a robust network to handle heavy loads. | Describes a network that is strong and resilient. |
Usage Rules for Adjectives Describing Networks
When using adjectives to describe networks, it’s important to adhere to standard English grammar rules. Here are some key guidelines:
- Placement: Adjectives typically precede the noun they modify. For example, “a secure network.”
- Linking Verbs: Adjectives can follow linking verbs like is, are, was, and were. For example, “The network is reliable.”
- Adverb Modification: Adverbs can modify adjectives to provide more detail. For example, “a highly efficient network.”
- Order of Adjectives: When using multiple adjectives, follow the general order of opinion, size, physical quality, shape, age, color, origin, and material.
- Hyphenation: Use hyphens for compound adjectives that come before the noun. For example, “a high-speed network.”
Common Mistakes When Using Adjectives for Networks
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using adjectives to describe networks:
- Incorrect Placement: Placing the adjective after the noun when it should come before.
- Incorrect: network secure
- Correct: secure network
- Misuse of Hyphens: Failing to hyphenate compound adjectives.
- Incorrect: high speed network
- Correct: high-speed network
- Incorrect Adjectives: Choosing the wrong adjective to describe the network.
- Incorrect: fast security
- Correct: secure network
- Redundancy: Using adjectives that repeat the meaning of the noun or other adjectives.
- Incorrect: network network
- Correct: local network
- Vagueness: Using adjectives that are too general and don’t provide specific information.
- Incorrect: good network
- Correct: efficient network
- Misuse of Commas: Incorrectly separating multiple adjectives.
- Incorrect: A reliable, secure,network
- Correct: A reliable, secure network
Practice Exercises
Test your understanding of adjectives for networks with these exercises. Fill in the blanks with the most appropriate adjective from the provided list.
Exercise 1: Choose the best adjective to describe a network that is easy to expand.
Options: scalable, secure, fast
Answer: scalable
Exercise 2: Choose the best adjective to describe a network that protects sensitive data.
Options: vulnerable, secure, slow
Answer: secure
Exercise 3: Choose the best adjective to describe a network with high data transfer rates.
Options: fast, unreliable, small
Answer: fast
Exercise 4: Correct the following sentence: “The network reliable ensures constant uptime.”
Answer: The reliable network ensures constant uptime.
Exercise 5: Correct the following sentence: “The company uses a high speed network.”
Answer: The company uses a high-speed network.
Advanced Topics
For a deeper understanding of adjectives for networks, consider these advanced topics:
- Network Architectures: Explore how different network architectures (e.g., SDN, NFV) influence the choice of adjectives.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Investigate how QoS parameters relate to performance-related adjectives.
- Network Security Protocols: Study how security protocols (e.g., TLS, IPSec) impact the use of security-related adjectives.
- Emerging Technologies: Analyze how new technologies (e.g., 5G, IoT) introduce new adjectives for describing networks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between “fast” and “high-bandwidth” when describing a network?
“Fast” generally refers to the speed of data transfer, while “high-bandwidth” refers to the capacity of the network to carry large amounts of data. A network can be fast but have limited bandwidth, or vice versa.
How do I choose the most appropriate adjective for a network?
Consider the specific characteristics you want to emphasize. Are you focusing on speed, security, size, or reliability? Choose an adjective that accurately reflects the most important aspects of the network.
Can I use multiple adjectives to describe a network?
Yes, but be mindful of redundancy and clarity. Use adjectives that provide unique and meaningful information, and follow the correct order of adjectives.
Conclusion
Using adjectives effectively to describe networks is essential for clear and precise communication. By understanding the different types and categories of adjectives, following usage rules, and avoiding common mistakes, you can accurately convey the characteristics, qualities, and attributes of various networks. Whether you are discussing network performance, security, topology, or purpose, the right adjectives will enhance your ability to articulate and analyze network-related concepts. Continue to practice and expand your vocabulary to master the art of describing networks with precision and clarity.



